คุณต้องการใช้อนุประโยคสัมพันธ์เพื่อทำให้การเขียนประโยคภาษาอังกฤษเป็นธรรมชาติและถูกต้องมากขึ้นหรือไม่? มาร่วมกับ Monkey เพื่อศึกษา วิธีการใช้ that, which, who, เคล็ดลับการจดจำอย่างรวดเร็ว ตัวอย่างประกอบที่ใช้ได้จริง และแบบฝึกหัดปฏิบัติอย่างละเอียดในบทความนี้
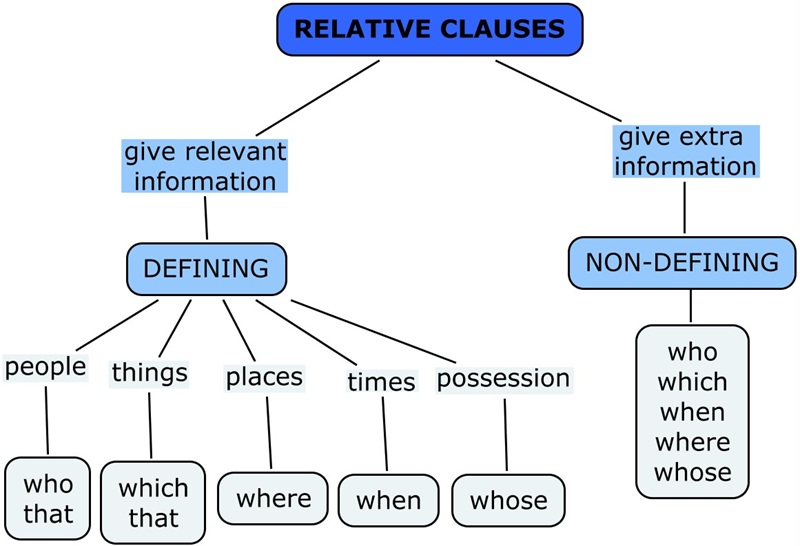
อนุประโยคสัมพันธ์คืออะไร?
อนุประโยคสัมพันธ์ (Relative Clause) คืออนุประโยคย่อยที่ใช้เพื่อขยายความนามที่อยู่ข้างหน้า ช่วยให้ประโยคมีความชัดเจนและละเอียดมากยิ่งขึ้น อนุประโยคนี้มักขึ้นต้นด้วย สรรพนามสัมพันธ์ (who, which, that) หรือ กริยาวิเศษณ์สัมพันธ์ (when, where, why)
-
ตัวอย่าง: She is the woman that I talked to yesterday. (เธอคือผู้หญิงที่ฉันได้คุยด้วยเมื่อวานนี้)
-
กลุ่มคำ “that I talked to yesterday” คืออนุประโยคสัมพันธ์ที่ขยายคำนาม “the woman”

ตาราง: ตำแหน่งของอนุประโยคสัมพันธ์ในประโยค
|
ตำแหน่งในประโยค |
คำอธิบาย |
โครงสร้าง |
ตัวอย่าง |
|
ตามหลังประธาน |
อนุประโยคสัมพันธ์ที่ใช้ขยายความประธานของประโยค |
S + (สรรพนามสัมพันธ์ / กริยาวิเศษณ์สัมพันธ์ + V + O) + V + O |
The teacher, who always encourages us, gave an inspiring speech today. (ครูผู้ซึ่งมักจะให้กำลังใจเราเสมอ ได้กล่าวสุนทรพจน์ที่สร้างแรงบันดาลใจในวันนี้) |
|
ตามหลังกรรม |
อนุประโยคสัมพันธ์ที่ใช้ขยายความกรรมของประโยค |
S + V + O + (สรรพนามสัมพันธ์ + S + V + O) |
The book I just finished reading, which was recommended by my professor, was helpful. (หนังสือที่ฉันเพิ่งอ่านจบ ซึ่งศาสตราจารย์ของฉันแนะนำ มีประโยชน์มาก) |
ประเภทของอนุประโยคสัมพันธ์ในภาษาอังกฤษ
มีอยู่ 2 ประเภทหลัก ๆ คือ:
-
อนุประโยคสัมพันธ์แบบกำหนดความหมาย (Defining Relative Clause)
-
อนุประโยคสัมพันธ์แบบไม่กำหนดความหมาย (Non-defining Relative Clause)
อนุประโยคสัมพันธ์แบบกำหนดความหมาย (Defining Clause)
ใช้เพื่อให้ข้อมูลที่จำเป็นในการระบุนามที่อยู่ข้างหน้า
หากไม่มีอนุประโยคนี้ ความหมายของประโยคจะไม่สมบูรณ์
ไม่มีเครื่องหมายจุลภาค ( , )
ตัวอย่าง:
-
The man who is sitting next to you is handsome. (ผู้ชายที่นั่งข้าง ๆ คุณนั้นหล่อ)
-
หากไม่มีอนุประโยคสัมพันธ์ “who is sitting next to you” เราจะไม่สามารถรู้ได้ว่า “the man” คือใคร
อนุประโยคสัมพันธ์แบบไม่กำหนดความหมาย (Non-defining Clause)
ใช้เพื่อให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมแก่นามที่อยู่ข้างหน้า
หากตัดออก ความหมายของประโยคก็ยังคงสมบูรณ์
มีเครื่องหมายจุลภาค ( , )
ตัวอย่าง:
-
Rosie, who is sitting next to you, is beautiful. (โรซี่ ผู้ที่นั่งข้าง ๆ คุณนั้นสวย)
-
แม้จะไม่มีอนุประโยคสัมพันธ์ “who is sitting next to you” แต่เราก็ยังรู้ได้ว่า “Rosie” คือใคร
การเปรียบเทียบ: อนุประโยคสัมพันธ์แบบกำหนดความหมาย vs ไม่กำหนดความหมาย
|
อนุประโยคกำหนดความหมาย |
อนุประโยคไม่กำหนดความหมาย |
|
จำเป็นต้องมีเพื่อทำให้ประโยคชัดเจน |
ไม่จำเป็น มีไว้เพื่อเสริมความหมาย |
|
หากตัดออก ประโยคจะไม่ชัดเจนหรือไม่สมบูรณ์ |
หากตัดออก ประโยคยังคงมีความหมายครบถ้วน |
|
ไม่มีเครื่องหมายจุลภาค (,) |
มีเครื่องหมายจุลภาค (,) |
|
ใช้ได้กับสรรพนามสัมพันธ์ทุกตัว |
ไม่สามารถใช้กับสรรพนามสัมพันธ์ “that” |
|
Mr. Smith, who is our CEO, will attend the meeting. (มิสเตอร์สมิธ ผู้ซึ่งเป็นซีอีโอของเรา จะเข้าร่วมการประชุม) |
The new office, which is located downtown, is very spacious. (สำนักงานใหม่ที่ตั้งอยู่ใจกลางเมือง มีพื้นที่กว้างขวางมาก) |
สรรพนามสัมพันธ์
|
สรรพนาม (Pronoun) |
หน้าที่ (Function) |
ตัวอย่าง (Example) |
|
Which |
ทำหน้าที่เป็นประธานหรือกรรมของอนุประโยคย่อย (สามารถละสรรพนามได้) ใช้แทนนามที่เป็นสิ่งของ หรือทั้งประโยคก่อนหน้า |
The report which was submitted yesterday contains valuable insights. (รายงานที่ส่งเมื่อวานมีข้อมูลเชิงลึกที่มีค่า) |
|
Who |
ทำหน้าที่เป็นประธานหรือกรรมของอนุประโยคย่อย (สามารถละสรรพนามได้) ใช้แทนนามที่เป็นบุคคล |
The manager who led the team to success received an award. (ผู้จัดการที่นำทีมไปสู่ความสำเร็จได้รับรางวัล) |
|
Whom |
ทำหน้าที่เป็นกรรม ใช้แทนนามที่เป็นบุคคล |
The client whom we met last week is interested in our services. (ลูกค้าที่เราเจอเมื่อสัปดาห์ที่แล้วสนใจบริการของเรา) |
|
That |
ทำหน้าที่เป็นประธาน ใช้แทนได้ทั้งคนและสิ่งของ |
The presentation that you prepared was well-received by the board. (การนำเสนอที่คุณเตรียมไว้ได้รับการตอบรับอย่างดีจากคณะกรรมการ) |
|
Whose |
อยู่หน้าคำนาม ใช้แทนความเป็นเจ้าของ |
The colleague whose idea was selected will lead the project. (เพื่อนร่วมงานที่ไอเดียของเขาได้รับเลือกจะเป็นผู้นำโครงการ) |
|
What |
ไม่ต้องมีนามนำหน้า ใช้ในความหมายว่า “สิ่งที่/สิ่งซึ่ง” โดยรวมความหมายของสรรพนามสัมพันธ์และสิ่งที่กล่าวถึงเข้าด้วยกัน |
What she needs is more time to finish the project. (สิ่งที่เธอต้องการคือเวลามากขึ้นเพื่อทำโครงการให้เสร็จ) |
กริยาวิเศษณ์สัมพันธ์ (Relative Adverbs)
|
กริยาวิเศษณ์ (Adverb) |
หน้าที่ (Function) |
ตัวอย่าง (Example) |
|
Where |
ใช้แทนนามที่เป็นสถานที่ |
The conference room where we usually hold meetings is being renovated. (ห้องประชุมที่เราใช้จัดการประชุมเป็นประจำกำลังถูกปรับปรุง) The office where I started my career is now one of the biggest companies in the city. (สำนักงานที่ฉันเริ่มต้นอาชีพ ปัจจุบันเป็นหนึ่งในบริษัทที่ใหญ่ที่สุดในเมือง) |
|
When |
ใช้แทนนามที่เป็นเวลา |
There was a time when we had to work late every day to meet deadlines.(ครั้งหนึ่งเราเคยต้องทำงานดึกทุกวันเพื่อให้ทันกำหนดเวลา) The moment when the project was approved felt like a huge achievement. (ช่วงเวลาที่โครงการได้รับการอนุมัติเป็นเหมือนความสำเร็จครั้งใหญ่) |
|
Why |
ใช้แทนคำว่า the reason / for that reason ใช้เพื่อบอกเหตุผล |
The reason why the client rejected the proposal was unclear.(เหตุผลที่ลูกค้าปฏิเสธข้อเสนอยังไม่ชัดเจน) They explained the reasons why the team failed to meet the deadline.(พวกเขาอธิบายเหตุผลว่าทำไมทีมไม่สามารถทำงานเสร็จทันกำหนดได้) |
อนุประโยคสัมพันธ์แบบย่อ (Reduced Relative Clause)
อนุประโยคสัมพันธ์ (Relative Clause) สามารถย่อให้สั้นลงได้ ซึ่งมักสร้างความสับสนให้ผู้เรียนในการสังเกตและวิเคราะห์ความหมายของประโยค
รูปแบบการย่อที่พบบ่อยที่สุดมี 2 แบบ:
-
ย่อโดยใช้ Present Participle (V-ing)
-
ย่อโดยใช้ Past Participle (V3/V-ed)
ย่อโดยใช้ Present Participle (V-ing)
ใช้เมื่อกริยาในอนุประโยคสัมพันธ์เป็นรูป Active Voice
สามารถตัดสรรพนามสัมพันธ์ออก
กริยาจะเปลี่ยนเป็นรูป V-ing
ตัวอย่าง:
The professor who teaches English Literature is leaving our university. (ศาสตราจารย์ที่สอนวรรณคดีอังกฤษกำลังจะออกจากมหาวิทยาลัยของเรา)
การย่อ:
-
The professor who teaches → teaching English Literature is leaving our university.
-
The professor teaching English Literature is leaving our university.
ย่อโดยใช้ Past Participle (V3/V-ed)
ใช้เมื่อกริยาในอนุประโยคสัมพันธ์เป็นรูป Passive Voice (be + V3/V-ed)
สามารถตัดสรรพนามสัมพันธ์และ “be” ออก
กริยายังคงเป็นรูป V3/V-ed
ตัวอย่าง:
The candidates who were chosen after the interview will have a field trip to our company. (ผู้สมัครที่ได้รับการคัดเลือกหลังการสัมภาษณ์จะได้ไปทัศนศึกษาที่บริษัทของเรา)
การย่อ:
-
The candidates who were chosen after the interview → chosen after the interview
-
The candidates chosen after the interview will have a field trip to our company.

ข้อควรระวังในการใช้อานุประโยคสัมพันธ์ (Relative Clause)
1. การใช้ that ในบางโครงสร้างประโยค
เมื่อมีคำนามผสมที่หมายถึงทั้งคนและสิ่งของ
He and his dog that have been together for 10 years are very famous in my hometown. (เขากับสุนัขของเขาที่อยู่ด้วยกันมา 10 ปี มีชื่อเสียงมากในบ้านเกิดของฉัน)
เมื่อใช้กับคำนามไม่เจาะจง เช่น nothing, everything, something
She blamed herself for everything that had happened. (เธอโทษตัวเองสำหรับทุกสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้น)
เมื่อใช้กับรูปขั้นสุด (superlative)
The Wimbledon men’s final was the best game of tennis that I’ve ever seen. (รอบชิงชนะเลิศวิมเบิลดันฝ่ายชายเป็นแมตช์เทนนิสที่ดีที่สุดที่ฉันเคยดูมา)
2. การวางตำแหน่งสรรพนามสัมพันธ์ (Relative Pronoun) ให้ถูกต้อง
ต้องวาง relative pronoun ไว้ติดกับคำนามที่มันแทน เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงความกำกวม
-
ผิด: I wore a ghost costume on Halloween Day, which is so scary. (ทำให้เข้าใจว่า วันฮาโลวีน น่ากลัว)
-
ถูก: I wore a ghost costume which is so scary on Halloween Day. (หมายถึง ชุดผี น่ากลัว)
3. อนุประโยคสัมพันธ์ต้องขยายคำนาม (noun หรือ noun phrase) และต้องวางถัดจากคำนามนั้นทันที
4. ในประโยคความซ้อน (complex sentence) ที่ใช้ relative clause
ต้องประกอบด้วยอย่างน้อย:
-
Independent clause (ประโยคหลัก)
-
Dependent clause (ประโยครอง)
5. ต้องมั่นใจว่าแต่ละอนุประโยคมีประธานและกริยา/กลุ่มกริยาครบถ้วน
และสามารถแยกออกมาเป็นประโยคเดี่ยวที่สมบูรณ์ได้
ตัวอย่าง:
-
That is the man who lives next door to me. (นั่นคือชายที่อาศัยอยู่ข้างบ้านฉัน)
-
My grandmother, who has just turned 80, is very healthy and active. (คุณยายของฉันซึ่งเพิ่งมีอายุครบ 80 ปี ยังแข็งแรงและกระฉับกระเฉงมาก)
แบบฝึกหัดประยุกต์
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1: เชื่อมประโยคด้วยอนุประโยคสัมพันธ์
(จงเชื่อมประโยคสองประโยคเป็นประโยคเดียว โดยใช้ who, which, that, where, whose)
-
The man is my teacher. He is standing over there.
-
The book is very interesting. I bought it yesterday.
-
This is the girl. Her father is a doctor.
-
I know the woman. She lives next door.
-
The film was boring. We saw it last night.
-
The house is very old. My grandparents live in it.
-
The students are working hard. They are preparing for the exam.
-
That’s the shop. I usually buy clothes there.
-
The boy broke the window. He is my cousin.
-
The car is new. It belongs to Mr. John.
คำตอบ:
-
The man who is standing over there is my teacher.
-
The book which I bought yesterday is very interesting.
-
This is the girl whose father is a doctor.
-
I know the woman who lives next door.
-
The film that we saw last night was boring.
-
The house where my grandparents live is very old.
-
The students who are preparing for the exam are working hard.
-
That’s the shop where I usually buy clothes.
-
The boy who broke the window is my cousin.
-
The car that belongs to Mr. John is new.
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2: เติมสรรพนามสัมพันธ์ให้ถูกต้อง
(เติม who, which, that, where, whose ลงในช่องว่าง)
-
The man ______ teaches us English is very kind.
-
The book ______ you lent me was very interesting.
-
I know the girl ______ father is a pilot.
-
The restaurant ______ we had dinner was expensive.
-
This is the house ______ I was born.
-
She is the person ______ helped me a lot.
-
The car ______ is parked outside is mine.
-
The boy ______ mother is a nurse studies in my class.
-
I have a friend ______ can speak five languages.
-
The movie ______ we watched yesterday was amazing.
คำตอบ:
-
who
-
which/that
-
whose
-
where
-
where
-
who
-
which/that
-
whose
-
who
-
which/that
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 3: ย่ออนุประโยคสัมพันธ์ (Reduced Relative Clause)
(เปลี่ยนประโยคที่มีอนุประโยคสัมพันธ์ให้เป็นประโยคที่มีวลี participle)
-
The man who is standing at the gate is my uncle.
-
The girl who is talking to Tom is my sister.
-
The students who are sitting in the room are learning English.
-
The house which was built last year is very modern.
-
The book which is lying on the table is mine.
-
The woman who lives next door is a doctor.
-
The road which connects the two villages is very narrow.
-
The boy who broke the window has just run away.
-
The people who are waiting for the bus look tired.
-
The car which was made in Japan is very expensive.
คำตอบ:
-
The man standing at the gate is my uncle.
-
The girl talking to Tom is my sister.
-
The students sitting in the room are learning English.
-
The house built last year is very modern.
-
The book lying on the table is mine.
-
The woman living next door is a doctor.
-
The road connecting the two villages is very narrow.
-
The boy breaking the window has just run away.
-
The people waiting for the bus look tired.
-
The car made in Japan is very expensive.
บทสรุป
ทฤษฎี Relative Clause – อนุประโยคสัมพันธ์ในภาษาอังกฤษ เป็นหัวข้อไวยากรณ์ที่ค่อนข้างซับซ้อน อย่างไรก็ตาม ประเด็นไวยากรณ์นี้ไม่ได้ยากเกินไป หากคุณเข้าใจทฤษฎีทั้งหมดอย่างชัดเจน รวมถึงวิธีการสร้างประโยคที่มีอนุประโยคสัมพันธ์ สำหรับเด็ก ๆ สามารถฝึกฝนเป็นประจำด้วยแอปพลิเคชัน Monkey Junior เพื่อพัฒนาทักษะภาษาอังกฤษของตนเองได้