Comparative adverbs help describe how two actions differ in manner, speed, frequency, or degree. Understanding how to form and use them correctly makes your sentences clearer and more precise. With the right rules and examples, you can apply comparative adverbs confidently in both speaking and writing.
What are comparative adverbs?
Comparative adverbs are words that compare how two actions are performed, highlighting differences in manner, speed, frequency, or degree. They modify verbs - not nouns, so they focus on the action rather than the qualities of a person or thing. Unlike comparative adjectives, which compare nouns, comparative adverbs strictly compare behaviors or performance.
Use comparative adverbs when you want to show that one action happens in a different way or to a different extent than another. They are helpful when comparing two subjects performing the same action or when emphasizing variations in intensity or frequency. In both writing and speaking, they make comparisons clearer and more precise.
Examples:
-
She worked more efficiently than her colleague.
-
The train arrived later than usual today.
-
He speaks English more fluently after months of practice.
-
The athlete ran faster than everyone expected.
-
They replied more politely in the second meeting.

How to form comparative adverbs
1. One-syllable adverbs
Most one-syllable adverbs form the comparative by adding -er to the base form. This rule applies to short adverbs that do not end in -ly, making them straightforward to recognize and use. It is commonly used with everyday adverbs like fast, hard, or late.
Examples:
-
She ran faster than her brother.
-
He worked harder this week to meet the deadline.
-
The bus arrived later than we expected.
2. Multi-syllable adverbs
Adverbs with two or more syllables form the comparative with more or less placed before the adverb. This structure keeps the sentence smooth and avoids unnatural endings. It is the standard pattern for most -ly adverbs.
Examples:
-
He explained the lesson more clearly during the review session.
-
They responded less politely than usual.
-
She moved more quietly so she wouldn’t wake the baby.
3. Irregular forms
Some adverbs have irregular comparative forms that do not follow the -er or more/less rules. These forms must be memorized because they change entirely in spelling or structure. The most common irregular adverbs include well → better and badly → worse.
Examples:
-
She sings better after taking vocal lessons.
-
He handled the situation worse than he expected.
-
The team performed better in the second half of the game.
Comparison structures with examples
1. Basic comparative structure
The basic structure for using comparative adverbs is S + V + comparative adverb + than + object. This pattern directly compares how two subjects perform an action. It is straightforward and widely used in both spoken and written English.
Examples:
-
She reads faster than her classmates.
-
The new machine operates more efficiently than the old one.
-
He reacts more quickly than most people in emergencies.
2. Comparative without “than”
Comparisons can also be made without “than”, especially when the second element is understood or implied. In such cases, writers may use expressions like as … as or simply omit the comparison target. This structure is common in conversational English.
Examples:
-
She works as carefully as a professional editor.
-
He speaks more confidently now.
-
The car runs less smoothly after the repair.
3. Degree modifiers with comparatives
Degree modifiers such as much, far, a bit, slightly, considerably help express how strong or weak a comparison is. They make sentences more precise by showing the extent of the difference. These modifiers are placed before the comparative adverb.
Examples:
-
She responded much more politely after understanding the issue.
-
The new software loads far faster than the previous version.
-
He completed the task slightly more carefully this time.

Common mistakes to avoid
1. Wrong formation
A frequent mistake is forming comparatives by adding -ly and then attaching -er, which results in incorrect structures like quickly-er or slowly-er. Learners often do this because they confuse adverbs ending in -ly with adjectives. Always check whether the adverb follows the more/less pattern instead of adding endings.
Examples:
-
She runs quicklyer than me. [Wrong]
-
She runs more quickly than me. [Right]
2. Misusing “more” with one-syllable adverbs without -ly
Another common error is using more before one-syllable adverbs that should take -er, such as fast, hard, or late. This usually happens when learners assume all adverbs need “more,” but many short ones follow the regular comparative pattern. Choosing the correct form helps keep your sentences natural and grammatically accurate.
Examples:
-
He finished the race more fast than I did. [Wrong]
-
He finished the race faster than I did. [Right]
-
She worked harder to complete the project. [Right]
|
Give your child a strong English foundation from the very beginning with Monkey Junior. Start learning through fun games, native audio, and smart AI tools–perfect for kids aged 0-11. Help them build real skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing step by step. Download Monkey Junior today and watch your child grow in confidence and English ability. |
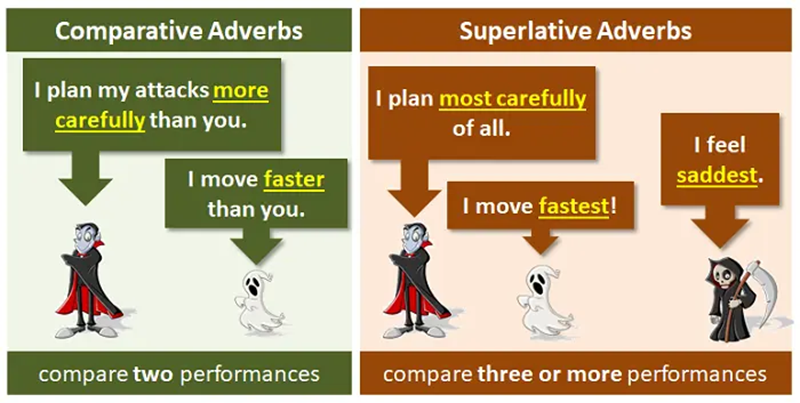
Comparative and superlative adverbs
1. Definition & purpose
Comparative and superlative adverbs show differences in how actions are performed, allowing you to express contrast or highlight the highest degree. Comparative adverbs compare two actions, while superlative adverbs compare three or more. These forms help you communicate performance, speed, accuracy, or intensity with greater precision.
2. Formation rules
Comparative adverbs usually follow -er for short adverbs and more/less + adverb for longer or -ly forms. Superlative adverbs use -est for one-syllable adverbs or most/least + adverb for multi-syllable forms. A small group of adverbs have irregular patterns, such as well → better → best and badly → worse → worst, and must be memorized.
3. Examples table
Below is a concise table showing common forms:
|
Base Adverb |
Comparative |
Superlative |
Example Sentence |
|
fast |
faster |
fastest |
She finished the task faster than before. |
|
hard |
harder |
hardest |
He trained the hardest during the final week. |
|
quickly |
more quickly |
most quickly |
The software loads more quickly after the update. |
|
slowly |
more slowly |
most slowly |
The machine operates most slowly in cold weather. |
|
well |
better |
best |
She performs best under pressure. |
|
badly |
worse |
worst |
He reacted worse than he should have. |
Comparative adverbs are simple but powerful tools for expressing differences in actions. When you master their forms and structures, your English becomes more accurate and natural. Regular practice will help you use comparative adverbs effortlessly in real communication.




.png)