Conditional sentences type 2 are essential in English grammar for expressing hypothetical or unreal situations in the present and future. Unlike real conditions, these sentences describe scenarios that are unlikely or impossible, helping learners sound more fluent and natural in both written and spoken English.
What are conditional sentences type 2?
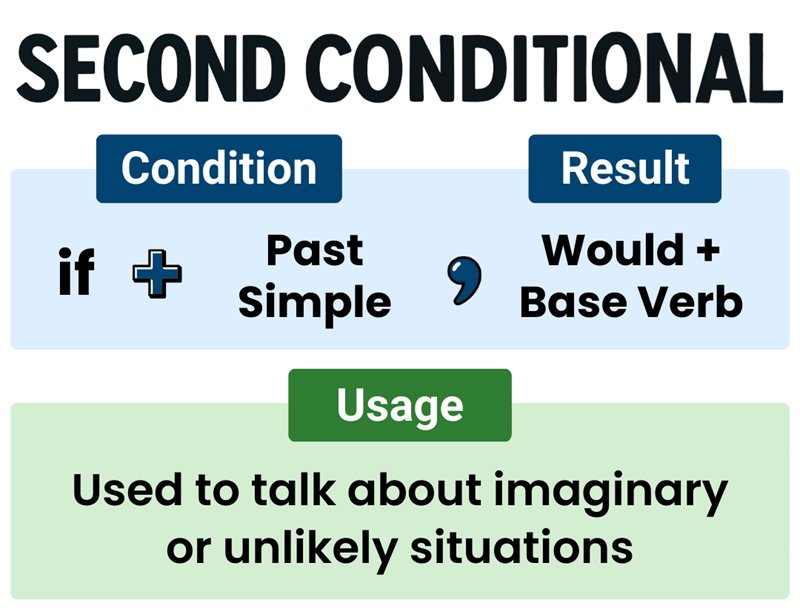
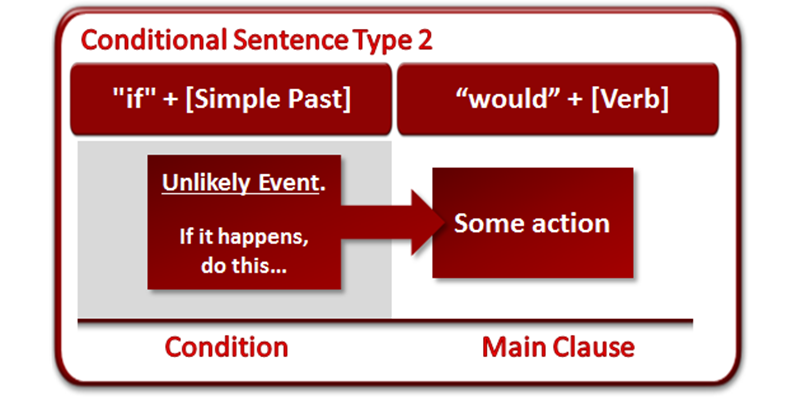
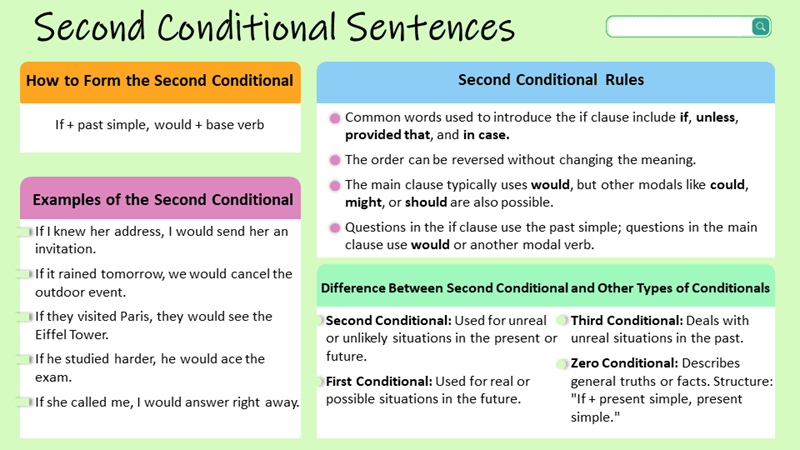
Conditional sentences type 2 are used to describe unreal or hypothetical situations in the present or future. These sentences outline conditions that are unlikely to happen or completely contrary to current facts, making them useful for imagining different outcomes or alternative realities. They typically follow the structure If + simple past, would + base verb, as in “If I had a million dollars, I would buy a house,” where the speaker does not actually have that money.
Type 2 conditionals matter because they allow speakers to express dreams, long-term wishes, and imagined scenarios with clarity. They are also essential for giving indirect advice, since the structure softens the tone and makes recommendations sound more polite and thoughtful. Additionally, they help create distance in polite requests or refusals, making communication smoother and more natural.
Compared with other conditional types, type 2 serves a unique function. Type 0 describes general truths or scientific facts, so its meaning is fully real and universal. Type 1 expresses real and possible future outcomes, meaning the condition still has a chance to occur. Type 3 refers to unreal past situations, imagining outcomes that can no longer change, while type 2 focuses on unreal present or future scenarios that are imagined but not entirely impossible to discuss.
Examples:
-
If I lived near the beach, I would swim every morning.
-
If she studied more, she would get better grades.
-
If we had a bigger house, we could host more guests.
-
If he were more patient, he might handle stress better.
-
If they knew the answer, they would tell you immediately.
Structure and grammar rules
1. Basic structure
Structure: If + simple past, … would/could/might + base verb
This structure shows an unreal condition in the present and a hypothetical result in the future. The simple past in the if-clause does not refer to real past time but signals distance from reality. For example, “If I knew her, I would call her” means the speaker does not know her now.
2. Use of “to be” in type 2 conditionals
Structure: If + subject + were, … would/could/might + base verb
In unreal conditions, were is traditionally used for all subjects, including “I,” “he,” and “she.” This form is preferred in formal writing and polite expressions, as in “If I were you, I would reconsider the idea.” Although it appears in casual speech, it remains the standard for accuracy.
3. Inversion form (advanced grammar)
Structure: Were + subject + complement, … would/could/might + base verb
This advanced form removes if and inverts the subject and verb to create a formal tone. Sentences like “Were I rich, I would travel the world” express the same meaning as regular type 2 conditionals. The inversion adds emphasis and is common in written or elevated speech.
4. Modals Variation in the Main Clause
Structure: … would/could/might/should + base verb
Different modal verbs change the meaning and tone of the result clause. Would expresses a logical or expected result, could show ability or possibility, and might suggest a less certain outcome. Should can appear to give advice or gentle recommendations, adding nuance to the statement.
Main uses of type 2 conditionals
Type 2 conditionals are versatile structures that help speakers express unreal, indirect, or softened meanings in everyday and formal communication.
-
Hypothetical Situations: Type 2 conditionals describe situations that are not true or unlikely in the present, allowing speakers to imagine different outcomes or alternate realities. They help paint scenarios that contrast with current facts in a clear and structured way. Example: “If I lived in London, I would visit museums every weekend.”
-
Advice or Suggestion: This form is often used to give polite and indirect advice that avoids sounding too direct or commanding. By framing guidance as a hypothetical condition, the speaker communicates respect and consideration. Example: “If I were you, I would rest more.”
-
Polite Requests or Offers: Type 2 conditionals soften requests and offers by creating emotional distance and reducing pressure on the listener. This makes the statement sound more diplomatic and professional in both written and spoken contexts. Example: “It would be great if you could send me the report.”
-
Refusal of Requests: Speakers also use type 2 forms to refuse requests gently without causing discomfort or appearing uncooperative. The hypothetical structure shifts focus to situational limitations rather than personal unwillingness. Example: “I would help you if I had more time.”
|
Give your child a strong English foundation from the very beginning with Monkey Junior. Start learning through fun games, native audio, and smart AI tools–perfect for kids aged 0-11. Help them build real skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing step by step. Download Monkey Junior today and watch your child grow in confidence and English ability. |
Practice exercises about conditional sentences type 2
Complete each sentence using the correct Type 2 conditional form.
-
If I __________ (have) more free time, I would learn how to paint.
-
She would buy that laptop if it __________ (be) cheaper.
-
If they lived closer, we __________ (visit) them more often.
-
He __________ (help) you if he knew the answer.
-
If we __________ (not / be) so busy, we might take a short holiday.
-
I would join the competition if I __________ (feel) more confident.
-
If you __________ (study) harder, you could pass the exam.
-
They might move abroad if their English __________ (be) better.
-
If it __________ (not / rain), we would go for a walk.
-
She __________ (cook) dinner for you if she had the ingredients.
-
If I __________ (be) you, I would talk to the manager about it.
-
We would travel more if we __________ (save) enough money.
-
If he __________ (exercise) regularly, he might feel healthier.
-
I __________ (buy) that dress if it suited me better.
-
If our house __________ (have) a bigger garden, we would host outdoor parties.
Answers:
-
had
-
were
-
would visit
-
would help
-
were not / weren’t
-
felt
-
studied
-
were
-
did not rain / didn’t rain
-
would cook
-
were
-
saved
-
exercised
-
would buy
-
had
Conditional sentences type 2 are powerful tools in English that allow you to express unreal, hypothetical, or imagined situations with confidence. By mastering their structure, common uses, and avoiding typical mistakes, learners can boost both accuracy and fluency in everyday conversation and academic exams. Practice regularly with examples to build instinctive familiarity.




.png)