Understanding how an Auxiliary Verb works is essential for mastering English grammar. These helping verbs support the main verb to express tense, mood, voice, and emphasis, making your sentences clearer and more accurate. In this guide, you’ll learn the definition, types, examples, and key grammar rules of auxiliary verbs so you can use them confidently in everyday communication.
What is an auxiliary verb?
An auxiliary verb is a helping verb that supports the main verb to express tense, aspect, voice, or mood. It adds grammatical information that the main verb cannot convey on its own. Without auxiliary verbs, English sentences would lack clarity in time, intent, and structure.
A main verb carries the core meaning of the sentence, describing the action or state. An auxiliary verb does not show the main action; instead, it helps form negatives, questions, continuous tenses, perfect tenses, and the passive voice. Together, they create complete and accurate sentence structures.
Auxiliary verbs ensure sentences are grammatically precise and easy to understand. They allow speakers to express complex ideas such as possibility, obligation, and progression. Mastering auxiliary verbs helps learners communicate more naturally and confidently in English.
Examples:
-
She is studying for her exam. — Primary auxiliary (be)
-
They have finished the project on time. — Primary auxiliary (have)
-
Do you know the answer to this question? — Primary auxiliary (do)
-
You should try a different approach next time. — Modal auxiliary (should)

Main types of auxiliary verbs
English auxiliary verbs fall into two main groups: primary auxiliary verbs and modal auxiliary verbs. Each group plays a different role in forming accurate and meaningful sentences.
1. Primary Auxiliaries
Primary auxiliary verbs include to be, to have, and to do, which help form questions, negatives, tenses, and the passive voice. They work directly with main verbs to express time, aspect, or grammatical structure.
Primary auxiliaries create key English tenses such as the continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous forms. They also support question formation and emphasis in statements.
Examples:
-
Present: She is working on her assignment.
-
Past: They were waiting outside the building.
-
Perfect: He has completed the task already.
-
Continuous: I am reading a new book this week.
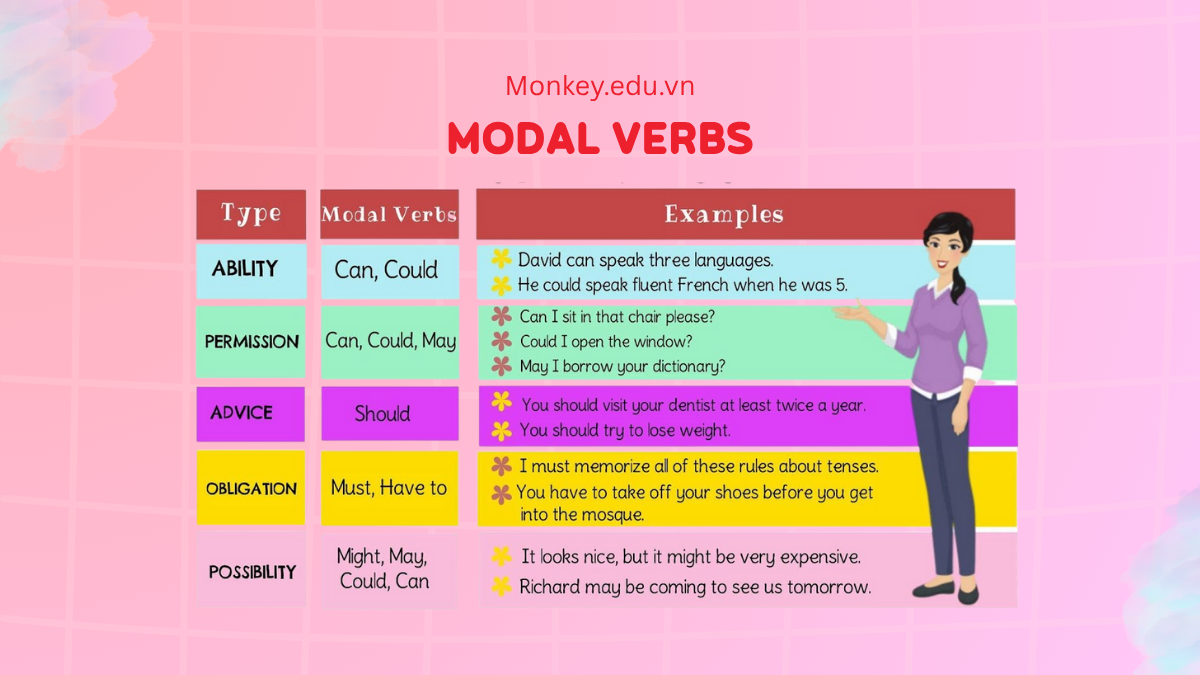
2. Modal Auxiliaries
Modal auxiliary verbs include can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would, and a few less common forms. These verbs add meaning related to possibility, obligation, ability, intention, or advice.
Modal auxiliaries allow speakers to express uncertainty, permission, requirements, and personal attitudes. They help shape the tone and intention of a sentence without changing form across tenses.
Common modals and meanings:
-
Can: ability or permission
-
Could: past ability or polite request
-
May: possibility or permission
-
Might: weaker possibility
-
Must: strong obligation or logical conclusion
-
Should: advice or expectation
-
Will: future intention or willingness
-
Would: polite request or hypothetical situations

How auxiliary verbs are used
Auxiliary verbs shape the structure and meaning of English sentences by helping form questions, negatives, tenses, and passive constructions. They also add emphasis or highlight specific parts of a sentence.
1. Questions & Negatives
Auxiliary verbs support question formation by moving before the subject, making the sentence clear and grammatically correct. They also enable negatives when combined with not, helping speakers express denial or refusal.
Examples:
-
Do you understand the instructions clearly?
-
She does not agree with the proposed plan.
2. Tense and Aspect
Auxiliary verbs create essential English tenses such as the perfect, continuous, and perfect continuous forms. They give sentences a sense of time, duration, or completion that main verbs cannot express alone.
Examples:
-
They have finished the assignment already.
-
He is working on a new project this week.
3. Passive Voice
In the passive voice, auxiliary verbs - especially forms of be shown that the subject receives the action rather than performing it. This structure shifts attention away from the doer and focuses on the action or result.
Examples:
-
The documents were prepared by the legal team.
-
The project is being reviewed by the committee.

4. Emphasis & Focus
Auxiliary verbs add emphasis when used before the main verb, helping highlight contrast or strong feelings. They also support focused statements, especially when correcting information or insisting on a point.
Examples:
-
I do appreciate your help on this task.
-
She did finish the report on time, despite the delays.
|
Give your child a strong English foundation from the very beginning with Monkey Junior. Start learning through fun games, native audio, and smart AI tools–perfect for kids aged 0-11. Help them build real skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing step by step. Download Monkey Junior today and watch your child grow in confidence and English ability. |
Comprehensive list of auxiliary verbs
Auxiliary verbs are grouped into primary auxiliaries and modal auxiliaries, each serving a different grammatical purpose. The tables below summarize the most common forms and include brief examples for clarity.
1. Primary auxiliary verbs
|
Primary Auxiliary |
Forms |
Example in Context |
|
Be |
am, is, are, was, were, be, being, been |
She is working on a new project. |
|
Have |
have, has, had |
They have finished their assignment. |
|
Do |
do, does, did |
Do you know the correct answer? |
2. Modal auxiliary verbs
|
Modal |
Core Meaning |
Example in Context |
|
can |
ability / permission |
She can solve the problem easily. |
|
could |
past ability / polite request |
Could you help me with this task? |
|
may |
possibility / permission |
We may start earlier today. |
|
might |
weak possibility |
He might join the team later. |
|
must |
strong obligation |
You must complete the form. |
|
shall |
suggestion / future intent |
We shall discuss this tomorrow. |
|
should |
advice / expectation |
You should check the details carefully. |
|
will |
future intention |
She will attend the workshop. |
|
would |
polite request / unreal situations |
Would you like some assistance? |
Mastering the Auxiliary Verb helps English learners build correct sentences, express ideas more clearly, and avoid common grammar mistakes. By understanding its definition, types, and usage rules, you can strengthen your writing and speaking skills effectively. Keep practicing with real examples and exercises to make auxiliary verbs a natural part of your language toolkit.




.png)