The subject in English is one of the core elements that forms a complete sentence. Understanding how subjects function helps learners build clear and grammatically correct sentences.
|
WATCH THE VIDEO SUMMARY OF THE ARTICLE |
What Is a Subject in English?
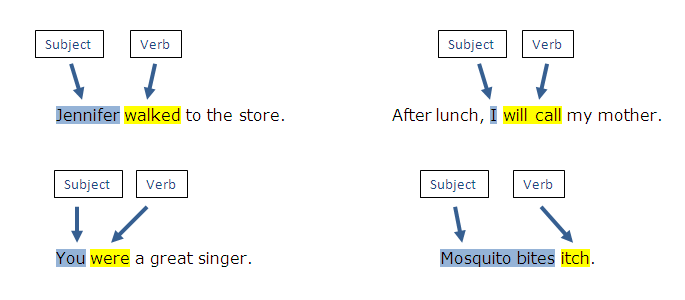
To begin, it’s essential to understand the basic role of the subject. A subject in English refers to the person, thing, or idea that performs or experiences the action of the verb. Without a subject, a sentence cannot be complete.
Examples:
-
Tom plays football.
-
The dog is barking.
-
Happiness matters.
The subject sets the foundation for the entire sentence structure.
Types of Subjects in English
Before identifying subjects in real sentences, it helps to learn their different forms. Subjects can appear as single words or long phrases, depending on what the sentence expresses.
1. Simple subject
A simple subject includes only the main word (usually a noun or pronoun) that the sentence is about.
Examples:
-
Birds fly.
-
She works hard.
Simple subjects make sentences straightforward and direct.
2. Complete Subject
A complete subject contains the simple subject and all the words describing it. This gives the sentence more detail.
Examples:
-
The tall man in the blue jacket is waiting.
-
My new laptop works perfectly.
-
Complete subjects help express clearer meaning.
3. Compound Subject
A compound subject includes two or more subjects connected by “and” or “or.” This type shows that multiple people or things share the action.
Examples:
-
Anna and Mark are studying.
-
Coffee or tea is fine.
-
Compound subjects allow for more complex sentence ideas.
4. Gerund or Infinitive as Subject
Sometimes, actions expressed by gerunds or infinitives function as subjects. This helps express general activities or habits.
Examples:
-
Reading helps improve focus.
-
To travel is my dream.
-
This structure is common in more formal writing.
5. Clause as Subject
A clause can also serve as the subject, especially when expressing ideas or statements.
Examples:
-
What she said surprised everyone.
-
How you behave reflects your character.
-
Clauses allow subjects to carry deeper meaning.

Position of Subjects in English Sentences
Knowing where subjects typically appear helps learners identify and use them correctly. Most English sentences follow the standard Subject + Verb + Object (SVO) pattern.
Examples:
-
The teacher explains the lesson.
-
My parents love traveling.
-
However, in some sentence types, the subject comes after the verb.
Examples:
-
Here comes the bus.
-
There are many options.
-
Recognizing these structures helps avoid confusion.
Subject–Verb Agreement
Before using subjects effectively, it’s important to master subject–verb agreement. This rule ensures that singular subjects use singular verbs, and plural subjects use plural verbs.
Examples:
-
The cat runs. (singular)
-
The cats run. (plural)
Special cases:
-
Everyone / someone / anybody → singular verb
-
Both / many / few → plural verb
-
Subjects joined by and → plural
-
Subjects joined by or / nor → verb agrees with the closest subject
Correct agreement ensures sentences sound natural and accurate.

Common Mistakes with Subjects in English
Learners often misidentify or misplace subjects. Reviewing typical mistakes helps avoid confusion.
|
Mistake |
Correct |
Explanation |
|
There is many problems. |
There are many problems. |
Verb must match real subject. |
|
Running fast make me tired. |
Running fast makes me tired. |
Gerund subject → singular. |
|
Anna and Tom is here. |
Anna and Tom are here. |
Compound subject → plural. |
|
The group are meeting. |
The group is meeting. |
Collective noun → usually singular. |
Understanding the rules helps eliminate these errors.
Examples of Subjects in Different Contexts
To apply the rules effectively, here are examples across common sentence types.
-
Statement: The restaurant opens at 7 AM.
-
Question: Who opened the door?
-
Negative sentence: My friend doesn’t like spicy food.
-
Complex sentence: What we decide today will affect the project.
Each structure highlights the importance of identifying the subject clearly.
Practice Exercises: Subject in English
Exercise 1: Identify the Subject
Find the subject in each sentence.
-
The little boy with curly hair is singing.
-
Swimming every morning keeps her healthy.
-
My parents and my sister are visiting soon.
-
What he said shocked everyone.
-
The group of students was late.
Exercise 2: Choose the Correct Verb
Select the correct verb form based on the subject.
-
Each of the players (is / are) ready.
-
The dogs in the yard (barks / bark).
-
Neither Tom nor his parents (was / were) informed.
-
Reading books (improves / improve) vocabulary.
-
My brother and I (enjoy / enjoys) hiking.
Exercise 3: Create Your Own Sentences
Write:
-
One sentence with a simple subject
-
One with a compound subject
-
One with a gerund as subject
Answer Key
Exercise 1:
-
The little boy with curly hair
-
Swimming every morning
-
My parents and my sister
-
What he said
-
The group of students
Exercise 2:
-
is
-
bark
-
were
-
improves
-
enjoy
Learn English Grammar with Monkey Junior
If you want a structured and intuitive way to master basic grammar concepts like the subject in English, Monkey Junior is an effective learning platform. The program explains sentence components through short lessons, vivid examples, and step-by-step activities that help learners recognize subjects naturally in context.
Monkey Junior also reinforces grammar through spaced repetition, pronunciation practice, and real-life sentence patterns, making it useful for both beginners and self-learners. With interactive lessons, quizzes, and progressive levels, Monkey Junior helps build a solid foundation in English grammar, vocabulary, and reading skills.
Start your child’s learning journey today with Monkey Junior and let them express their emotions in English confidently and naturally.

Conclusion
Mastering the subject in English is essential for building correct sentences, ensuring clear communication, and improving overall grammar skills. By understanding the different types of subjects, their positions, and the rules of subject–verb agreement, learners can express ideas more confidently. Combined with consistent practice and supportive tools like Monkey Junior, anyone can strengthen their grammar and use English more effectively.




.png)