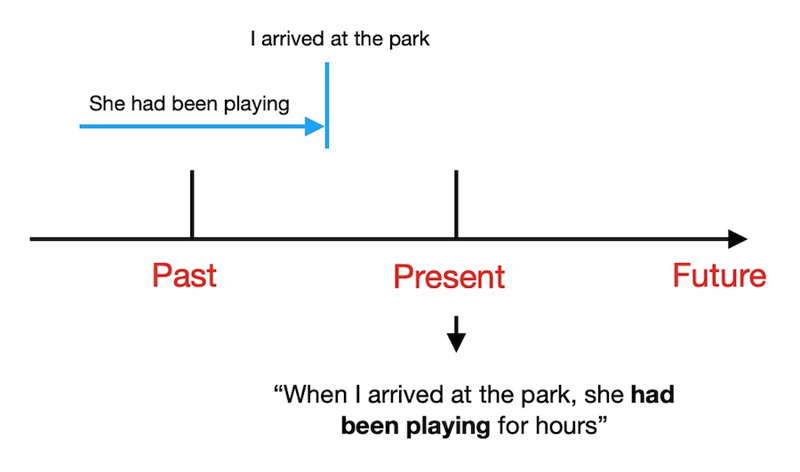
The past perfect continuous tense is an advanced English tense used to describe long actions that continued up to a specific moment in the past. This complete guide explains its structure, uses, common mistakes, and examples, helping you understand how and when to use the past perfect continuous tense with accuracy and confidence.
What is the past perfect continuous tense?
The past perfect continuous tense describes an action that began earlier in the past and continued up to another specific moment or event in the past. It highlights not only when the action happened but also its ongoing nature before that later point.
We use this tense to show how long something had been happening before a result or change occurred in the past, placing strong focus on duration. It helps provide context, explain causes, and make past narratives clearer by showing that an action was still in progress before another past event interrupted or ended it.
Examples:
-
She had been working at the company for five years before she decided to change careers.
-
They were exhausted because they had been walking all afternoon.
-
The streets were wet; it had been raining for hours before the storm finally stopped.
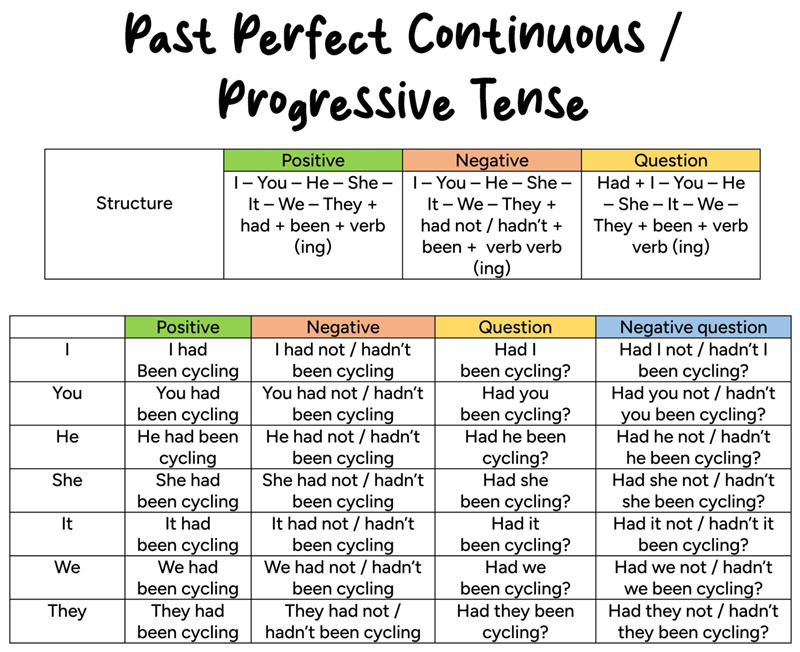
Past perfect continuous structure and formula
|
Form |
Structure |
Example |
|
Positive |
had been + verb-ing |
She had been studying English for two years before she moved abroad. |
|
Negative |
hadn’t been + verb-ing |
He hadn’t been sleeping well before the doctor gave him advice. |
|
Question |
Had + subject + been + verb-ing? |
Had they been waiting long when the bus finally arrived? |
1. Positive form
The past perfect continuous in positive form is built with had been + verb-ing, and it shows that a past action was already in progress before another moment in the past. This structure stays the same for all subjects, which makes it simple and consistent.
2. Negative form
The negative form uses had not (hadn’t) been + verb-ing to show an action that did not continue up to a later past point. It often explains absence of progress or results in a past situation.
3. Question form
The question form follows Had + subject + been + verb-ing?, and it asks about the duration or continuity of an action before another past event. It works with WH- words when more detail is needed, such as Why, How long, or Where.
Uses of the past perfect continuous tense
1. Duration before another past event
This tense shows how long an action had continued before another action or moment arrived in the past. It helps highlight time length clearly and adds depth to past descriptions.
Examples:
-
She had been teaching for ten years before she opened her own school.
-
They had been traveling for months before they finally reached home.
2. Cause & effect in the past
The tense explains a past result that happened because an earlier action was ongoing, making the link between cause and effect easy to see. It often reveals feelings, physical states, or visible outcomes.
Examples:
-
He was exhausted because he had been running in the heat.
-
Her clothes were soaked because she had been walking in the rain.
3. Context for interrupted actions
It describes a continuous past action that was happening right up until another event interrupted or ended it. This use adds flow and clarity when telling stories about the past.
Examples:
-
She had been reading when the phone suddenly rang.
-
They had been arguing when their friends arrived.
4. Repeated or parallel actions
This tense can show repeated or ongoing activities happening before another past moment, sometimes involving more than one subject or action. It helps express patterns or simultaneous progress in the past.
Examples:
-
The team had been practicing every evening before the tournament began.
-
Students had been working on different projects before the deadline was announced.

Past perfect continuous vs. Similar tenses
1. Past continuous vs. Past perfect continuous
The past continuous describes an action that was in progress at a specific time in the past, without linking it to an earlier duration. In contrast, the past perfect continuous shows an action that began before another past event and continued up to that later point.
Examples:
-
Past Continuous: “She was cooking dinner at 6 p.m.”
-
Past Perfect Continuous: “She had been cooking dinner for an hour when the guests arrived.”
2. Present perfect continuous vs. Past perfect continuous
The present perfect continuous connects a past action to the present, showing that the activity began earlier and is still happening now or has recently stopped. Meanwhile, the past perfect continuous remains fully in the past, showing an action that ended before another past event.
Examples:
-
Present Perfect Continuous: “They have been studying for two hours, and they are still working.”
-
Past Perfect Continuous: “They had been studying for two hours before the test started.”
|
Give your child a strong English foundation from the very beginning with Monkey Junior. Start learning through fun games, native audio, and smart AI tools–perfect for kids aged 0-11. Help them build real skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing step by step. Download Monkey Junior today and watch your child grow in confidence and English ability. |
Practice exercises
1. Fill-in-the-blank sentences
Complete each sentence using the past perfect continuous tense:
-
She __________ (study) English for months before she took the exam.
-
They __________ (wait) for over an hour when the doors finally opened.
-
His hands were dirty because he __________ (fix) the bike all morning.
-
We __________ (look) for that document before we found it in the drawer.
-
The kids __________ (play) outside until the rain started.
2. Rewrite the sentences
Rewrite each sentence using the past perfect continuous tense to show duration:
-
She painted for two hours before dinner.
-
They worked on the project until midnight.
-
He drove for a long time before reaching the hotel.
3. Short quiz (choose the correct answer)
1. Which sentence correctly uses the past perfect continuous tense?
a. She had been cooking when we arrived.
b. She has been cooking when we arrived.
c. She was cooking when we arrived.
2. Which sentence best shows duration before another past event?
a. They had been training hard before the match started.
b. They were training hard before the match started.
c. They trained hard before the match started.
3. Which sentence describes cause and effect?
a. He slept early because he was tired.
b. He was tired because he had been exercising all day.
c. He is tired because he works late.
Answers
Exercises 1:
-
had been studying
-
had been waiting
-
had been fixing
-
had been looking
-
had been playing
Exercises 2:
-
She had been painting for two hours before dinner.
-
They had been working on the project until midnight.
-
He had been driving for a long time before reaching the hotel.
Exercises 3:
-
a
-
a
-
b

Mastering the past perfect continuous tense will make your past storytelling clearer and more natural, especially when showing duration or cause and effect. Keep practicing with real examples and exercises from this guide to build a strong command of the past perfect continuous tense in English.




.png)