Personal pronouns are essential building blocks in English because they replace nouns and make communication clearer and more natural. This guide explains what personal pronouns are, how they work, and the rules you need to use them correctly.
What are personal pronouns?
Personal pronouns are words that replace specific nouns to avoid repetition and make sentences clearer. They stand in for people, objects, or groups that are already known from context.
Unlike nouns, which name things directly, personal pronouns refer back to someone or something previously mentioned. This shift allows sentences to flow more naturally and reduces unnecessary repetition.
Personal pronouns also express grammatical “person,” indicating who is speaking, who is being spoken to, or who is being discussed. They additionally show number (singular or plural) and, in some cases, gender to match the noun they replace.

Types of personal pronouns
Personal pronouns can be grouped into several categories based on their grammatical role. The two most common ways to classify them are by person and number.
1. Person categories
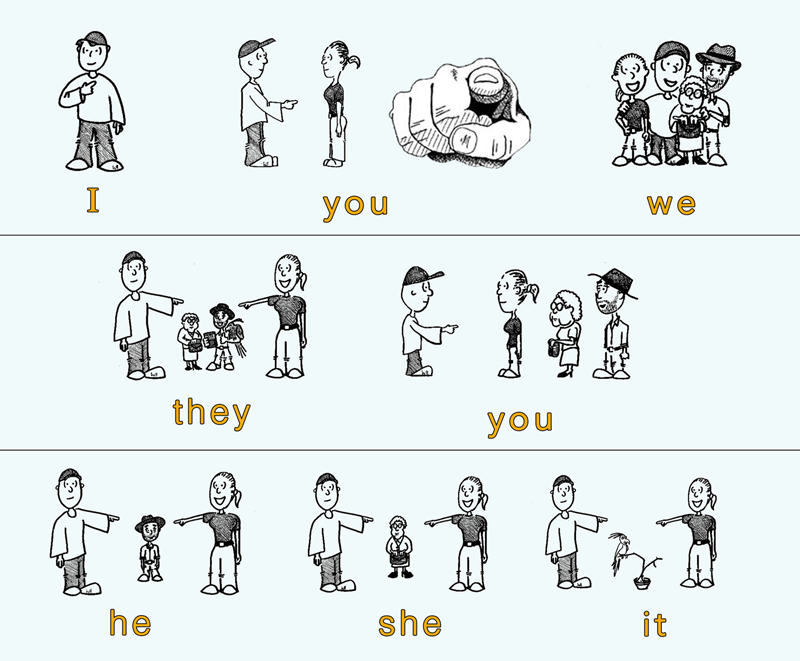
Personal pronouns reflect the “person” involved in a conversation, showing who is speaking and who is being spoken to. They are divided into first person, second person, and third person.
-
First-person pronouns refer to the speaker or a group including the speaker, such as I or we. These forms help express personal viewpoints or shared experiences.
-
Second-person pronouns refer to the listener, most commonly you. English uses you for both singular and plural contexts, depending on the situation.
-
Third-person pronouns refer to people or things being discussed, such as he, she, it, or they. These pronouns create distance between the speaker and the subject of the sentence.
2. Number
Personal pronouns also show whether they represent one person or thing or more than one. This distinction appears in both subject and object forms.
-
Singular pronouns (e.g., I, he, she, it) refer to a single individual or object. They help identify one specific entity in a sentence.
-
Plural pronouns (e.g., we, you, they) refer to groups of people or things. They indicate that the reference includes multiple members within the same idea or context.
Subject and Object pronouns
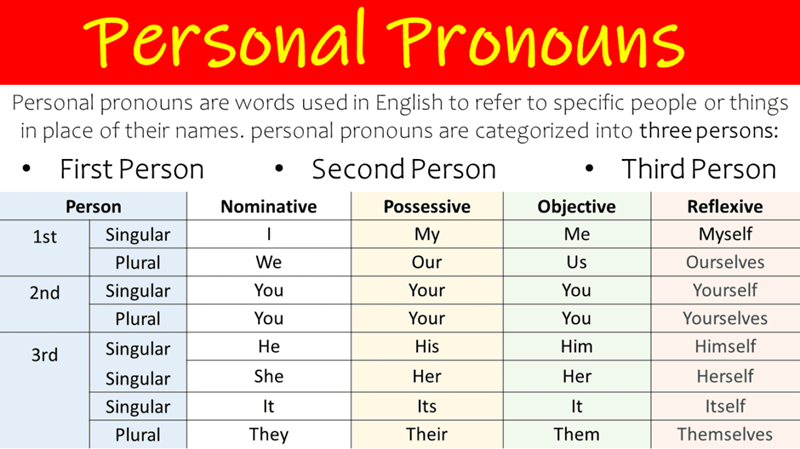
Personal pronouns change form depending on whether they act as the subject or the object in a sentence. Understanding this distinction helps keep sentences grammatically clear and natural.
1. Subject Pronouns
Subject pronouns are used when the pronoun performs the action of the verb. The main subject pronouns in English are I, you, he, she, it, we, and they.
These pronouns clarify who is taking action in a sentence.
Examples:
-
She works from home during the summer.
-
They finished the project on time.
2. Object Pronouns
Object pronouns are used when the pronoun receives the action of the verb or follows a preposition. The primary object pronouns are me, you, him, her, it, us, and them.
These pronouns show who or what is affected by the action in a sentence.
Examples:
-
The teacher called him to answer the question.
-
The manager spoke with us after the meeting.

Personal pronoun rules
Personal pronouns follow several grammatical rules to ensure clarity and accuracy in communication. These rules help readers understand exactly who or what a pronoun refers to.
1. Agreement with antecedents
A personal pronoun must match the noun it replaces in person, number, and when relevant, gender. This agreement prevents confusion and keeps the reference clear in the sentence.
If a pronoun doesn’t align with its antecedent, the sentence may sound ungrammatical or ambiguous. Writers often double-check this match when editing.
2. Capitalization rules
In English, the pronoun “I” is always capitalized, no matter where it appears in the sentence. This rule is unique among personal pronouns and applies even in informal writing.
Other personal pronouns, such as he, she, or they, are only capitalized at the beginning of a sentence or in special contexts like titles. This distinction keeps written English consistent and easy to read.
3. Using “you” for singular and plural
English uses “you” for both singular and plural forms, which can create ambiguity without context. Speakers often rely on tone, situation, or added words like you all or you guys to clarify the intended meaning.
Because “you” serves multiple roles, learners must pay attention to how it functions in a sentence. Despite this flexibility, the form of the pronoun itself never changes.
Practice exercises
Exercise 1: Choose the Correct Personal Pronoun
Select the pronoun that completes each sentence correctly.
-
___ am excited to start the new project. (I / Me)
-
The teacher asked ___ to submit the assignment early. (us / we)
-
___ said she would join the meeting later. (Her / She)
-
Could you help ___ with this task? (they / them)
-
___ are going to the museum this weekend. (We / Us)
Exercise 2: Replace the Noun with a Personal Pronoun
Rewrite each sentence using the correct personal pronoun.
-
Anna forgot her umbrella. → ______
-
I saw my cousins at the park. → ______
-
The manager called Michael and me to the office. → ______
-
The laptop isn’t working today. → ______
-
Emma and I finished the report early. → ______
Exercise 3: Identify the Pronoun Type
Label each underlined pronoun as subject, object, or possessive.
-
They arrived before noon. → ______
-
The gift was for her. → ______
-
That book is mine. → ______
-
I saw them at the conference. → ______
-
He prepared the presentation. → ______
|
Give your child a strong English foundation from the very beginning with Monkey Junior. Start learning through fun games, native audio, and smart AI tools–perfect for kids aged 0-11. Help them build real skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing step by step. Download Monkey Junior today and watch your child grow in confidence and English ability. |
Answers
Exercise 1:
-
I
-
us
-
She
-
them
-
We
Exercise 2:
-
She
-
Them
-
Us
-
It
-
We
Exercise 3:
-
Subject
-
Object
-
Possessive
-
Object
-
Subject

Understanding personal pronouns helps you write and speak more clearly by showing exactly who or what you are referring to. By learning their types, forms, and rules, you can use personal pronouns confidently in any English context.




.png)







