Mastering the difference between present simple and present continuous helps learners describe routines, ongoing actions, and real-time situations with clarity. This guide explains the rules, common uses, and examples of both tenses, followed by practical exercises to strengthen your understanding.
What are present simple and present continuous?
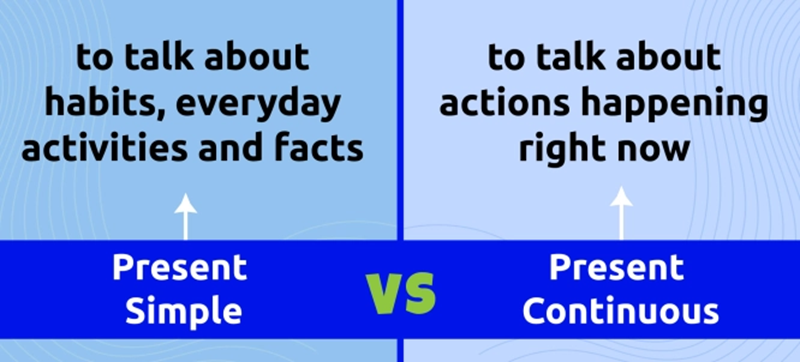
The present simple and present continuous are two core English tenses used to describe actions in the present, but they focus on different types of time. One shows general truth or routine, while the other highlights actions in progress or temporary situations.
1. Present simple overview
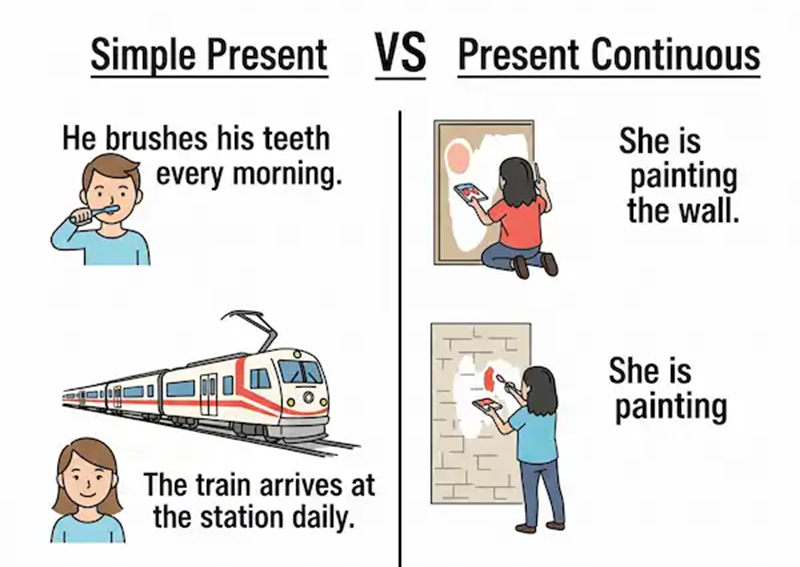
The present simple describes actions that are regular, repeated, or universally true. It expresses stable facts that do not depend on the moment of speaking.
We use the present simple for habits, daily routines, schedules, and scientific facts. It also appears when describing permanent situations or general attitudes.
Examples:
-
The sun rises in the east.
-
She drinks coffee every morning.
2. Present continuous overview
The present continuous describes actions happening right now or around the current period of time. It emphasizes progress, change, or temporary states.
We use the present continuous for ongoing activities, temporary conditions, and future arrangements that are already planned. It also helps express irritation with repeated actions when used with “always.”
Examples:
-
He is studying for his exam right now.
-
They are meeting the client tomorrow.
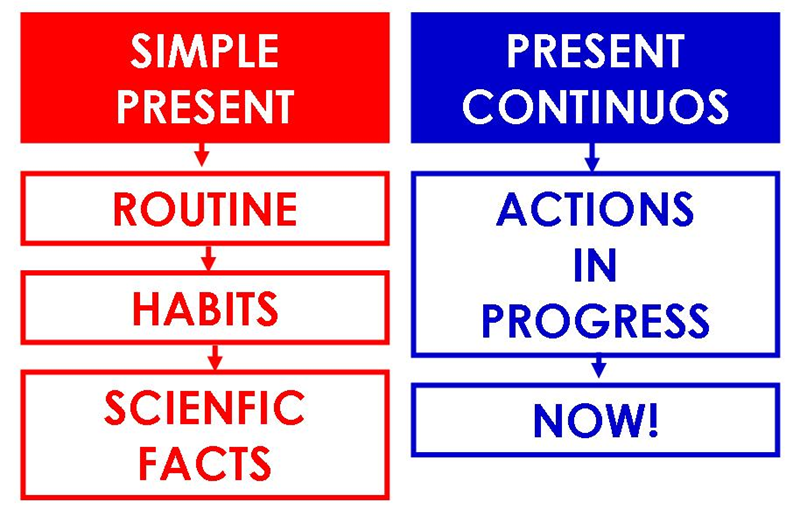
Usage comparison (side-by-side)
The present simple describes stable, repeated, or factual situations, while the present continuous focuses on actions happening now or temporary states. This table highlights how each tense functions in common contexts.
|
Use |
Present Simple |
Present Continuous |
|
Facts / general truths |
Used for statements that remain true over time. |
Not used because facts are not ongoing actions. |
|
Routines / habits |
Describes actions that happen regularly or repeatedly. |
Not used because habits are not actions in progress. |
|
Current actions |
Not used because the action is not happening at this exact moment. |
Describes actions occurring while the speaker is speaking. |
|
Temporary situations |
Not used for short-term or changing conditions. |
Used for situations that are temporary or developing. |
|
Future plans |
Sometimes used for fixed schedules such as timetables. |
Used for personal plans or arrangements that are already decided. |
Sentence structure & forms
The two tenses use different structures to show whether an action is regular or happening now. Mastering their forms helps learners build accurate sentences in everyday communication.
1. Present Simple Forms
Affirmative
The present simple uses the base form of the verb for all subjects except the third person singular.
Example: They work in a hospital.
Negative
We form the negative with do not (don’t) or does not (doesn’t) followed by the base verb.
Example: She doesn’t like spicy food.
Questions
Questions use Do/Does + subject + base verb to ask about habits or general truths.
Example: Do you play tennis?
Third person singular rules (-s, -es, -ies)
For he/she/it, regular verbs add -s, verbs ending in -ch, -sh, -ss, -x, -o add -es, and verbs ending in consonant + y change y → ies.
Example: He watches TV, She studies English.
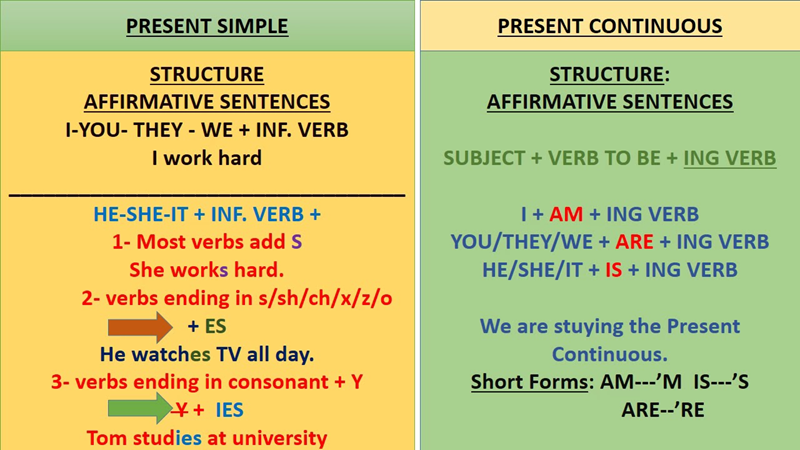
2. Present Continuous Forms
Affirmative
The present continuous uses am/is/are + V-ing to show actions happening now or around the present.
Example: They are cooking dinner.
Negative
We form the negative with am/is/are + not + V-ing to express actions that are not in progress.
Example: He isn’t working today.
Questions
Questions follow the pattern Am/Is/Are + subject + V-ing to ask about ongoing activities.
Example: Are you listening?
V-ing formation rules
We add -ing to most verbs, drop the final e for verbs like make → making, and double the final consonant after a stressed short vowel as in run → running.
Example: write → writing, plan → planning.
|
Give your child a strong English foundation from the very beginning with Monkey Junior. Start learning through fun games, native audio, and smart AI tools–perfect for kids aged 0-11. Help them build real skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing step by step. Download Monkey Junior today and watch your child grow in confidence and English ability. |
Signal words & time expressions
Signal words help identify whether an action is habitual or happening at the present moment. They provide strong clues for choosing between the present simple and the present continuous.
1. Present simple signal words
Present simple signal words include always, often, usually, every day, and other frequency adverbs. These expressions show routines or repeated actions that happen regularly over time.
Example: She usually wakes up at 6 a.m.
2. Present continuous signal words
Present continuous signal words include now, at the moment, right now, currently, which indicate actions unfolding as we speak or within a temporary period. They highlight that the situation is not permanent.
Example: He is currently working on a new project.
Practice exercises
These exercises help reinforce the difference between the present simple and the present continuous. Each activity focuses on accuracy, common patterns, and typical usage.
1. Choose the correct form
Select the correct verb form: present simple or present continuous.
-
She (works / is working) at a design company.
-
They (are studying / study) for their exam right now.
-
Tom usually (takes / is taking) the bus to school.
-
Listen! The birds (sing / are singing) in the garden.
-
I (don’t understand / am not understanding) this question.
2. Fill in the blanks
Use the correct form of the verb in parentheses.
-
My parents ________ (visit) us every weekend.
-
He ________ (not watch) TV at the moment.
-
The store usually ________ (open) at 9 a.m.
-
We ________ (have) dinner right now.
-
She ________ (study) English online this month.
3. Match with rule category
Match each sentence with its correct rule:
|
1. The Earth orbits the sun. 2. I’m meeting my friend after work. 3. She always forgets her keys. 4. They are staying at a hotel this week. 5. He is calling you right now. |
A. Habit B. Action happening now C. Temporary situation D. General truth E. Future arrangement |
Answers
Exercises 1:
-
works
-
are studying
-
takes
-
are singing
-
don’t understand
Exercises 2:
-
visit
-
is not watching
-
opens
-
are having
-
is studying
Exercises 3:
1 → D
2 → E
3 → A
4 → C
5 → B
Understanding when to use present simple and present continuous allows you to communicate everyday actions and current activities more accurately. Review the rules, study the examples, and complete the practice exercises to build stronger, more confident grammar skills.




.png)