The present continuous tense is one of the most commonly used verb tenses in English, especially when talking about actions happening right now or around the present time. This guide explains its definition, uses, structure, and real examples to help you understand and apply the tense with confidence.
What is the present continuous tense?
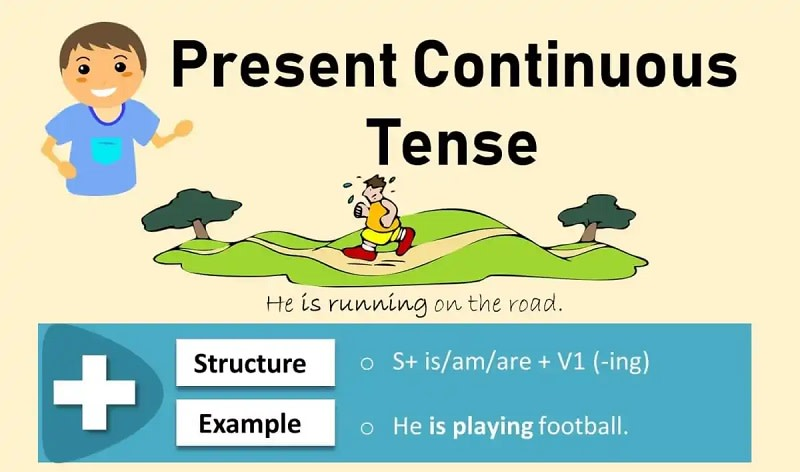
The present continuous tense is a tense used to describe actions that are happening right now at the moment of speaking. It shows that the activity has started but is not yet finished.
This tense also describes temporary situations, even if the action is not happening exactly right now. It highlights activities that are true around the present time, but not permanent.
Example: Christine is warming up the car.

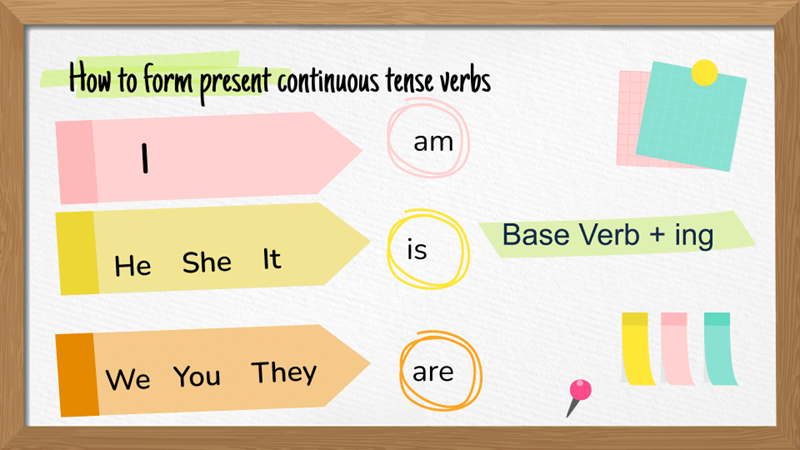
Present continuous tense formula
The present continuous tense is formed using the verb “to be” (am/is/are) plus the base verb + –ing. It changes depending on the subject and sentence type.
1. Affirmative form
Structure: S + am/is/are + V-ing
This form states an action that is happening right now or around the present. It shows the subject performing the action in progress.
Examples:
-
I am studying English now.
-
She is cooking dinner at the moment.
-
They are playing football in the yard.
2. Negative form
Structure: S + am/is/are + not + V-ing
This form is used to show that an action is not happening at the present moment. It simply denies an activity in progress.
Examples:
-
I am not working today.
-
He is not watching TV right now.
-
We are not traveling this week.
3. Question form
Structure: Am/Is/Are + S + V-ing?
This form is used to ask whether an action is happening now or during this period of time. It places the verb “to be” before the subject to form a question.
Examples:
-
Are you listening to me?
-
Is she coming to the party tonight?
-
Am I speaking too fast?
Present continuous tense uses
The present continuous tense has several key functions in daily communication. It helps describe what is happening now, what is temporary, and even future plans.
1. Actions Happening Now
We use the present continuous to describe actions that are occurring right at the moment of speaking. These actions are in progress and not yet completed.
Examples:
-
She is typing a report right now.
-
The students are taking a test at the moment.
-
I am talking to you on the phone.
2. Temporary actions
This tense expresses actions or situations that are true for a short period, even if they are not happening this exact second. It emphasizes change or a temporary lifestyle.
Examples:
-
He is living with his parents this month.
-
We are working from home this week.
-
My sister is studying French these days.
3. Actions happening around now
We use it to talk about activities that are ongoing within a general present period, not just at the exact moment of speaking. These actions often describe long-term projects or ongoing processes.
Examples:
-
They are building a new hospital in town.
-
I am reading a fantastic book these days.
-
She is training to become a nurse.
4. Future plans and arrangements
The present continuous refers to fixed or planned future actions, usually involving schedules or personal arrangements. Time expressions like tonight, tomorrow, or next week are common.
Examples:
-
We are meeting our friends tomorrow evening.
-
I am flying to Singapore next month.
-
She is starting a new job on Monday.
5. Annoying habits with “Always”
This tense can describe habits that happen repeatedly and are annoying or surprising, often showing irritation. It is typically used with the adverb “always.”
Examples:
-
He is always interrupting people.
-
They are always complaining about something.
-
You are always losing your keys.
Present continuous vs present simple
The present continuous describes actions happening now or temporary situations, while the present simple expresses habits, facts, and routines. Choosing the right tense depends on whether the action is temporary and in progress or permanent and repeated.
1. When to use each tense
Use the present continuous for actions in progress at the moment of speaking or around the present time. Use the present simple for facts, regular habits, daily routines, and things that are always true.
2. Comparison table
|
Feature |
Present Continuous |
Present Simple |
|
Time Focus |
Now / around now |
Always / usually / often |
|
Action Type |
Temporary, changing |
Permanent, regular |
|
Structure |
am/is/are + V-ing |
V1 / V1-s |
|
Signal Words |
now, at the moment |
always, every day |
|
Example Meaning |
Action in progress |
Habit or routine |
Example sentences showing the difference:
-
She is studying for her exams this week → temporary action in progress.
-
She studies every night before bed → regular habit.
-
I am working from home today → short-term situation.
-
I work in an office → permanent job fact.
-
They are traveling around Europe this month → temporary activity.
-
They travel abroad every summer → repeated routine.
|
Give your child a strong English foundation from the very beginning with Monkey Junior. Start learning through fun games, native audio, and smart AI tools–perfect for kids aged 0-11. Help them build real skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing step by step. Download Monkey Junior today and watch your child grow in confidence and English ability. |
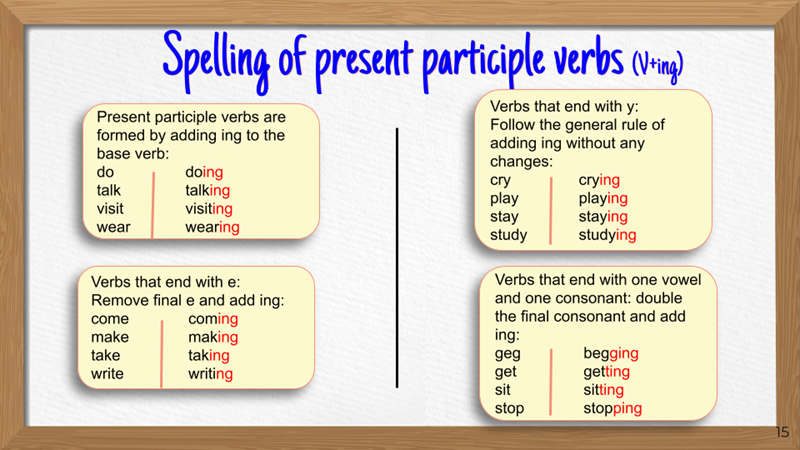
Present continuous V-ing spelling rules
These spelling rules explain how verbs change before adding -ing in the present continuous tense. They help ensure accuracy and avoid common errors in writing.
1. Verbs ending with “e”
If a verb ends with a silent “e,” drop the “e” and add -ing. This rule keeps pronunciation smooth and natural.
Examples:
-
make → making
-
write → writing
-
drive → driving
2. Doubling consonants
When a verb ends with a single vowel + a single consonant, double the final consonant before adding -ing. This happens only if the verb is one syllable or the final syllable is stressed.
Examples:
-
run → running
-
sit → sitting
-
begin → beginning
3. “ie → y” rule
For verbs ending in “ie,” change “ie” to “y” before adding -ing. This prevents awkward spelling combinations and keeps the word readable.
Examples:
-
die → dying
-
lie → lying
-
tie → tying
Practice exercises
These exercises help reinforce the structure and uses of the present continuous tense. They train learners to form sentences correctly and recognize common patterns.
1. Fill in the Blanks
Complete each sentence using the present continuous form of the verb in brackets. Focus on using am/is/are + V-ing.
-
She ________ (cook) dinner right now.
-
They ________ (watch) a movie at the cinema.
-
I ________ (study) for my exam this week.
-
He ________ (not work) today.
-
We ________ (travel) around Europe this month.
2. Make questions
Rewrite the prompts as present continuous questions. Place am/is/are before the subject.
-
you / listen / to the teacher?
-
she / work / tonight?
-
they / play / football now?
-
I / speak / too fast?
-
he / study / at the library today?
3. Error correction task
Each sentence contains a mistake in the present continuous form. Rewrite each sentence correctly.
-
She are playing the guitar.
-
I am go to school now.
-
They is working on a project.
-
We are not study today.
-
He are reading a book right now.
Answers
Exercises 1:
-
is cooking
-
are watching
-
am studying
-
is not working
-
are traveling
Exercises 2:
-
Are you listening to the teacher?
-
Is she working tonight?
-
Are they playing football now?
-
Am I speaking too fast?
-
Is he studying at the library today?
Exercises 3:
-
She is playing the guitar.
-
I am going to school now.
-
They are working on a project.
-
We are not studying today.
-
He is reading a book right now.
Mastering the present continuous tense will make your English sound more natural, accurate, and fluent in everyday communication. Keep reviewing the structure, practice regularly, and use the examples in this guide to apply the tense correctly in any situation.




.png)







