The simple past tense is one of the most important grammar topics for anyone learning English. It helps you talk clearly about actions that happened and ended in the past.
In this easy guide, you will learn the definition, rules, and examples of the simple past tense step by step. With support from Monkey, mastering this tense becomes simple and practical for everyday use.
What is the simple past tense?
The simple past tense is used to talk about actions or events that happened and ended in the past. It focuses on when something happened, not on its result now.
We use the simple past when the action is completely finished before the present moment. The time can be mentioned or clearly understood from context.
Examples:
-
I visited my grandparents last weekend.
-
She finished her homework an hour ago.
Common time expressions with the simple past include yesterday, last night, two days ago, and in 2020. These words help show that the action belongs to the past.
Example: They moved to London in 2020.

How to form the simple past tense
The simple past tense is formed by changing the base verb into its past form. This depends on whether the verb is regular or irregular.
1. Regular verbs
For regular verbs, add -ed to the base form. This rule works for most English verbs.
Examples:
-
work → worked.
-
play → played.
2. Irregular verbs
Irregular verbs do not follow a fixed rule, so their past forms must be memorized. Each verb changes in its own way.
Examples:
-
go → went.
-
see → saw.
-
eat → ate.
3. Spelling rules for -ed
If a verb ends in -e, just add -d.
Example: live → lived.
If a verb has one vowel + one consonant at the end, double the consonant and add -ed.
Example: stop → stopped.
If a verb ends in -y after a consonant, change -y to -ied.
Example: study → studied.
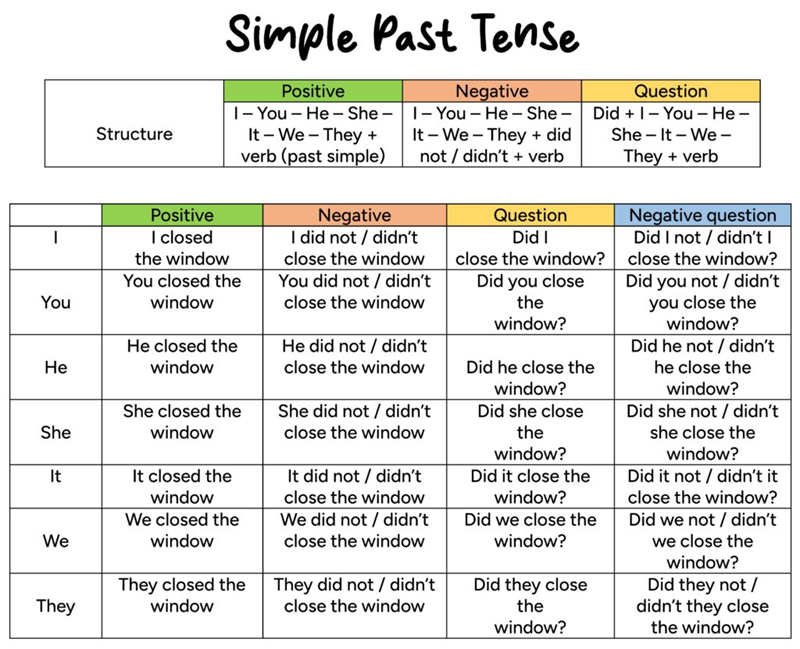
Sentence structure in the simple past
The simple past has clear patterns for affirmative sentences, negatives, and questions. Once you know them, forming sentences becomes easy.
1. Affirmative sentences
Use subject + past verb (V2/ed) to state a completed action. This form shows what happened in the past.
Example: I visited my grandma.
2. Negative sentences
Use subject + did not (didn’t) + base verb to make negatives. The main verb stays in its base form.
Example: She didn’t like the movie.
3. Questions
Use Did + subject + base verb? to ask about past actions. The verb does not change after did.
Example: Did you finish your homework?
|
Give your child a strong English foundation from the very beginning with Monkey Junior. Start learning through fun games, native audio, and smart AI tools–perfect for kids aged 0-11. Help them build real skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing step by step. Download Monkey Junior today and watch your child grow in confidence and English ability. |
Uses of the simple past tense
The simple past tense is used to talk about actions or situations that were completed in the past. It is one of the most common tenses in everyday English.
1. Completed actions in the past
Use the simple past for actions that started and finished at a specific time in the past. The time may be stated or implied.
Example: I called her yesterday.
2. A series of past actions
Use the simple past to describe several actions that happened one after another in the past. This is common in stories and narratives.
Example: He opened the door, walked in, and sat down.
3. Past habits or states
Use the simple past to talk about habits or states that were true in the past but are not true now. Often, words like always or often appear.
Example: We played soccer after school.
4. Storytelling and narratives
The simple past is widely used to tell stories, jokes, and past events. It helps move the story forward.
Example: Once upon a time, a king lived in a small village.
Simple past vs Present perfect
The simple past and the present perfect both talk about past actions, but they are used in different situations. The key difference is whether the time is finished or still connected to the present.
Comparison table:
|
Feature |
Simple Past |
Present Perfect |
|
Main use |
Completed actions at a finished time in the past. |
Past actions with a connection to the present. |
|
Time reference |
A specific time is stated or implied. |
No specific time is mentioned. |
|
Common time words |
yesterday, last night, ago, in 2020 |
ever, never, already, yet, just |
|
Focus |
When the action happened. |
The result or experience now. |
|
Form |
subject + V2/ed |
subject + have/has + V3 |
|
Example |
I finished the report yesterday. |
I have finished the report. |
Practice exercises
Use these exercises to practice forming the simple past tense. Focus on both regular and irregular verbs.
1. Fill in the blanks
Complete each sentence using the correct simple past form of the verb in brackets.
-
She ___ (visit) her aunt yesterday.
-
We ___ (finish) the test an hour ago.
-
They ___ (go) to the beach last weekend.
-
He ___ (buy) a new phone last night.
-
I ___ (study) English after dinner.
2 Change to negative
Rewrite each sentence in the negative form using did not or didn’t.
-
I watched the game last night.
-
She called me this morning.
-
They completed the project on time.
-
We enjoyed the concert yesterday.
-
He found his keys in the car.
3. Make questions
Change each sentence into a question using Did.
-
You met him after work.
-
She sent the email yesterday.
-
They enjoyed the party.
-
He fixed the computer last night.
-
You understood the lesson.
4. Short answers
Give short answers to the questions below. Use Yes, I did or No, I didn’t.
-
Did you finish your homework last night?
-
Did she arrive on time?
-
Did they understand the lesson?
-
Did he call you yesterday?
-
Did you watch the movie?

Answers
Exercises 1:
-
She visited her aunt yesterday.
-
We finished the test an hour ago.
-
They went to the beach last weekend.
-
He bought a new phone last night.
-
I studied English after dinner.
Exercises 2:
-
I didn’t watch the game last night.
-
She didn’t call me this morning.
-
They didn’t complete the project on time.
-
We didn’t enjoy the concert yesterday.
-
He didn’t find his keys in the car.
Exercises 3:
-
Did you meet him after work?
-
Did she send the email yesterday?
-
Did they enjoy the party?
-
Did he fix the computer last night?
-
Did you understand the lesson?
Exercises 4:
-
Did you finish your homework last night? → Yes, I did. / No, I didn’t.
-
Did she arrive on time? → Yes, she did. / No, she didn’t.
-
Did they understand the lesson? → Yes, they did. / No, they didn’t.
-
Did he call you yesterday? → Yes, he did. / No, he didn’t.
-
Did you watch the movie? → Yes, I did. / No, I didn’t.
The simple past tense is essential for describing past events with clarity and confidence. By understanding its rules and practicing with real examples, you can use it naturally in both speaking and writing.
Keep reviewing and practicing to build strong grammar habits. With helpful lessons from Monkey, you can master the simple past tense and move closer to fluent English.



.png)







