The present perfect tense is one of the most commonly used verb tenses in English, especially when talking about past experiences that connect to the present. In this guide, you’ll learn the present perfect tense definition, structure, uses, and clear examples to help you understand and use it confidently in daily communication.
What is the present perfect tense?
The present perfect tense describes actions or events that happened in the past but still connect to the present moment. It focuses on the result or impact now, rather than the exact time something occurred.
This tense is different from the past simple because past simple talks about a finished action at a specific time in the past, while present perfect talks about past actions with present relevance and no exact time given.
Examples:
-
I have finished my homework.
-
She has lived here for ten years.
-
They have visited London many times.
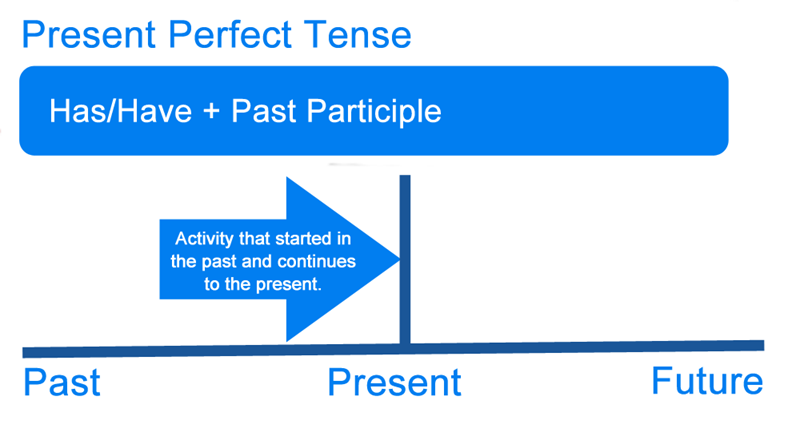
Structure of the present perfect tense
The present perfect tense uses have/has + past participle to connect a past action to a present outcome. It helps show what someone has achieved, experienced, or completed up to now.
1. Affirmative Form (+)
Formula: Subject + have/has + past participle
Use this form to talk about actions or events that are completed and relevant to the present moment.
Examples:
-
I have seen that movie before.
-
She has written three emails today.
-
They have finished the project.
2. Negative Form (-)
Formula: Subject + have/has + not + past participle
This form shows something has not happened or not been completed up to this moment.
Examples:
-
I have not eaten breakfast yet.
-
He has not called me today.
-
We have not decided what to do.
3. Interrogative Form (?)
These forms are used to ask whether an action has happened or to request more details about it.
(1) Yes/No Questions
Formula: Have/Has + subject + past participle?
This form checks if something has happened up to now.
Examples:
-
Have you finished your homework?
-
Has she arrived yet?
(2) Wh-Questions
Formula: Wh-word + have/has + subject + past participle?
Use this form to ask for specific information about the action.
Examples:
-
Where have you been?
-
How long has he worked here?
-
What have they done today?

How to use the present perfect tense
The present perfect tense is used to show how past actions connect to the present in different ways. Below are the main situations where English speakers naturally use this tense.
1. Life experience (no specific time)
Use the present perfect to talk about life experiences without mentioning when they happened. The exact time is not important; the experience itself matters.
Examples:
-
I have visited Japan twice.
-
She has never tried sushi.
-
They have met many famous people.
2. Unfinished Actions Until Now
Use it for actions that started in the past and continue up to the present, often with for or since. It highlights ongoing situations that are still true now.
Examples:
-
I have lived here for ten years.
-
He has worked at this company since 2018.
-
We have known each other since childhood.
3. Recent events with present results
Use this tense to describe recent actions that affect the present moment, often with words like just, already, or yet. The focus is on the result we can see or feel now.
Examples:
-
She has just finished her homework.
-
They have already eaten dinner.
-
He has not arrived yet.
4. Change over time
Use the present perfect to show how someone or something has changed from the past to now. It highlights development, growth, or transformation.
Examples:
-
My English has improved a lot.
-
The city has become more crowded over the years.
-
Technology has advanced quickly.
5. Repeated Actions Up to Now
Use it for actions that have happened several times from the past until now and may continue in the future. It emphasizes frequency and ongoing possibility.
Examples:
-
I have seen that movie three times.
-
She has visited London many times.
-
They have called me several times today.
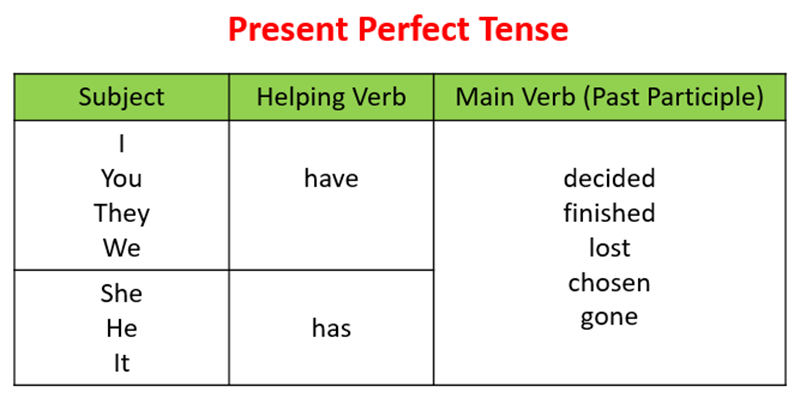
Present perfect vs past simple
The present perfect talks about past actions with a current connection, while the past simply describes actions completed at a specific time in the past. Use the table below to quickly see how they differ.
|
Point of Comparison |
Present Perfect Tense |
Past Simple Tense |
|
Meaning |
Past action linked to the present |
Past action finished with no link to now |
|
Time Reference |
No specific time mentioned |
Specific time stated or understood |
|
Form |
Have/has + past participle |
Verb in past form (V2) |
|
Focus |
Result or experience matters now |
Time and completion matter |
|
Typical Words |
already, yet, just, ever, never, since, for |
yesterday, last week, in 2015, two days ago |
|
Duration Use |
Yes, with actions continuing to now |
No, used for ended actions |
|
Questions |
Have/has + subject + PP? |
Did + subject + V1? |
|
Lifestyle Context |
General experiences up to now |
One-time actions in the past |
When to use each tense:
-
Use the present perfect when the time is not mentioned or still relevant to the present, especially for experience and ongoing situations.
-
Use the past simple when the action took place at a specific time in the past and is completely finished.
|
Give your child a strong English foundation from the very beginning with Monkey Junior. Start learning through fun games, native audio, and smart AI tools–perfect for kids aged 0-11. Help them build real skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing step by step. Download Monkey Junior today and watch your child grow in confidence and English ability. |
Practice exercises
These exercises help confirm your understanding of how the present perfect tense works in real contexts. Try to answer without looking back at the rules to test what you truly know.
1. Multiple choice
Choose the correct option:
1. She ____ her homework already.
A. has finished
B. finished
C. finish
2. I ____ that movie three times.
A. have seen
B. saw
C. see
3. They ____ in London since 2015.
A. lived
B. have lived
C. lives
4. He ____ the news yet.
A. hasn’t heard
B. didn’t hear
C. hasn’t hear
5. We ____ to France last summer.
A. have been
B. went
C. have gone
2. Fill the blanks
Use the present perfect form of the verbs in brackets.
-
She ______ (write) five emails today.
-
I ______ (not see) him this week.
-
They ______ (travel) to many countries.
-
He ______ (just finish) his lunch.
-
We ______ (live) here for ten years.
3. Rewrite sentences
Rewrite the sentences using the present perfect tense.
-
I started working here in 2020. I still work here.
-
She finished her project. She still has the result now.
-
They visited Japan in the past, many times.
-
He began learning English when he was a child and continues now.
-
I ate lunch, so I am not hungry anymore.

Answers
Exercises 1:
-
A. has finished
-
A. have seen
-
B. have lived
-
A. hasn’t heard
-
B. went
Exercises 2:
-
She has written five emails today.
-
I have not seen him this week.
-
They have traveled to many countries.
-
He has just finished his lunch.
-
We have lived here for ten years.
Exercises 3:
-
I have worked here since 2020.
-
She has finished her project.
-
They have visited Japan many times.
-
He has learned English since he was a child.
-
I have eaten lunch.
Mastering the present perfect tense is essential for expressing unfinished actions, life experiences, and recent changes naturally in English. With the right structure, common signal words, and real-life examples, you can apply the present perfect tense accurately and communicate more fluently and confidently.




.png)







