The simple future tense is an essential English grammar structure used to talk about events, predictions, and decisions that will happen after the present moment. In this guide, you’ll learn the full simple future tense definition, structure, common uses, and practical examples to help you communicate future ideas clearly and confidently.
Definition of simple future tense
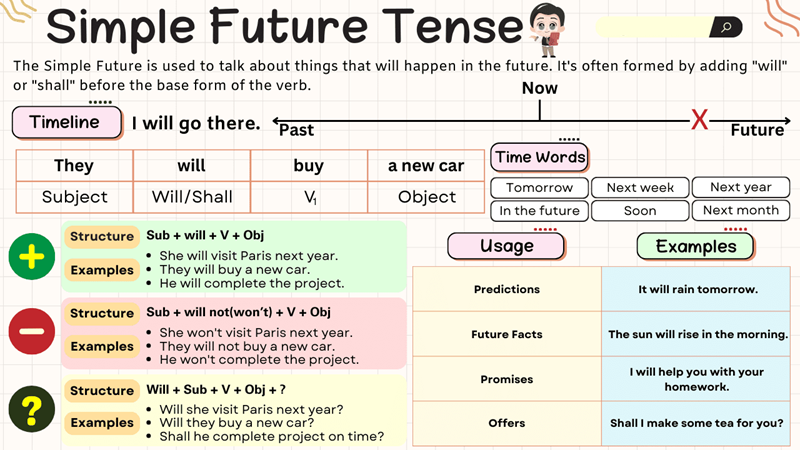
The simple future tense describes an action or state that will happen after the present moment. It uses the modal verb “will” to express future events in a direct, uncomplicated way.
Example: I will call you later.
Compared with other future forms, the simple future is used for neutral predictions, quick decisions, and promises. In contrast, “be going to” shows planned actions, while the present continuous expresses arranged or scheduled future events.
Examples:
-
I’m going to visit my aunt this weekend.
-
We are meeting the manager tomorrow.

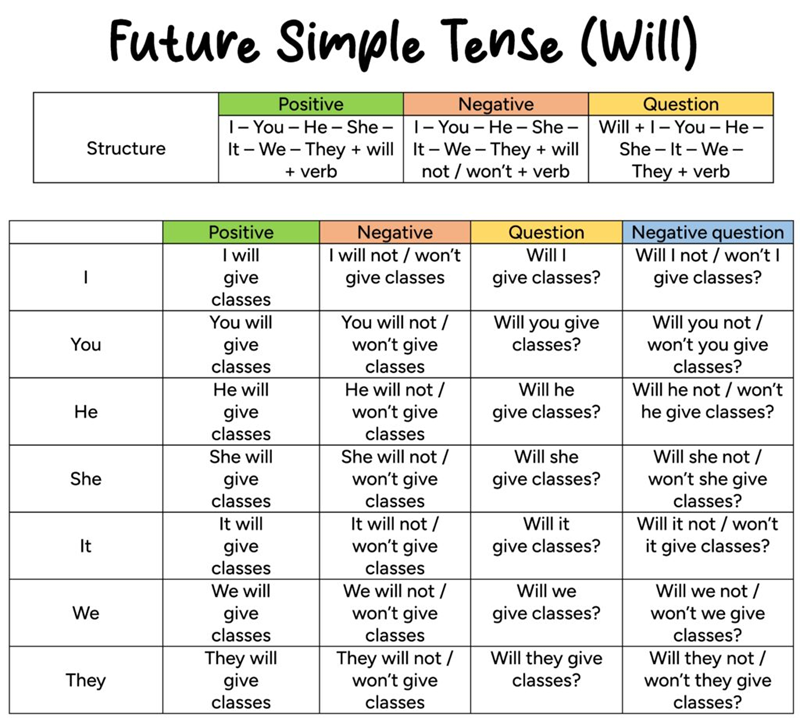
Formula & structure of simple future tense
The simple future tense uses the modal verb “will” for all subjects. The table below summarizes the structure, explanation, and examples in a single, easy-to-skim layout.
|
Form |
Structure |
Explanation |
Example |
|
Affirmative |
Subject + will + base verb |
Used to express a future action or intention in a clear, straightforward way. |
She will start her new job tomorrow. |
|
Negative |
Subject + will not (won’t) + base verb |
Shows that something is not expected to happen; won’t is common in daily use. |
They won’t attend the meeting. |
|
Interrogative |
Will + subject + base verb? |
Used to ask about future plans, intentions, or expected events. |
Will you join us for lunch? |
When to Use the Simple Future Tense
The simple future tense is used to talk about events that have not happened yet but are expected to occur. It is especially useful when discussing predictions, decisions, plans, or questions about the future.
1. Actions in the Future
Use the simple future tense to describe actions scheduled to happen or facts you know will be true later. These statements often highlight certainty about future events.
Example: The conference will start at 8 a.m.
2. Predictions
This tense expresses predictions based on personal belief, intuition, or limited evidence. It does not require a clear plan or concrete data.
Example: I think it will rain this evening.
3. Spontaneous decisions
Use will for decisions made instantly, often as a reaction to a situation or new information. These choices are not pre-planned.
Example: I’ll answer the phone.
4. Offers & promises
The simple future tense is commonly used when offering help, volunteering to do something, or making a commitment. It conveys intention and willingness.
Example: I will help you finish the report.
5. Questions about the future
Use will to form yes/no questions or wh- questions when asking about future actions, plans, or events. This structure works with all subjects and keeps the verb in its base form.
Examples: Will you travel next month? / What will we do next?
Common Signal Words
Certain time expressions frequently appear with the simple future tense because they point clearly to events that have not happened yet. These words help readers recognize that the action is expected to occur later in time.
Common signal words and phrases include tomorrow, next week, soon, later, someday, in the future, and in a few minutes. They often appear at the beginning or end of a sentence to emphasize when the action will happen.
Example: She will call you soon.
Simple future vs other future forms
Different future forms express different levels of certainty, planning, or timing, so choosing the right one depends on the speaker’s intention. The simple future tense is the most neutral and flexible option for referring to future events.
1. Simple Future vs “Be Going To”
Use be going to for planned actions or predictions supported by evidence. Meanwhile, the simple future tense often expresses spontaneous decisions or neutral predictions.
Example: Look at those clouds—it's going to rain.
2. Simple future vs present simple / present continuous
The present simple is used for official schedules or timetables, while the present continuous describes personal plans or arrangements already in place. The simple future tense, in contrast, expresses general future actions without a fixed plan.
Example: The train leaves at 6 a.m. (present simple for schedules)
3. Simple future vs future continuous / future perfect
The future continuous highlights an action that will be happening at a specific time in the future, while the future perfect focuses on an action that will be completed by a certain point. These forms give more detail about the timing or progression of future events than the simple future.
Example: By next month, I will have finished the project. (future perfect)

Practice exercises
The exercises below help learners review how the simple future tense works in different structures. Each task focuses on accuracy, clarity, and correct use of will.
1. Fill in the blanks
Use will + base verb to complete each sentence.
-
She ________ (visit) her grandparents this weekend.
-
I ________ (send) you the document after lunch.
-
They ________ (not join) the event tonight.
-
We ________ (meet) the new manager tomorrow.
-
He ________ (help) you carry those boxes.
2. Rewrite the sentences
Rewrite each sentence using the simple future tense.
-
I plan to call him later. → ______________________________
-
They are not ready to leave yet. → ______________________________
-
She plans to buy a new laptop. → ______________________________
-
We think they are late. → ______________________________
-
I decide to take a break. → ______________________________
3. Question formation
Form a question using will based on the statement given.
-
You will travel next month. → ______________________________
-
She will study abroad next year. → ______________________________
-
They will need more time. → ______________________________
-
He will cook dinner tonight. → ______________________________
-
We will move to a new office. → ______________________________
|
Give your child a strong English foundation from the very beginning with Monkey Junior. Start learning through fun games, native audio, and smart AI tools–perfect for kids aged 0-11. Help them build real skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing step by step. Download Monkey Junior today and watch your child grow in confidence and English ability. |
Answers
Exercises 1:
-
will visit
-
will send
-
will not join / won’t join
-
will meet
-
will help
Exercises 2:
-
I will call him later.
-
They will not leave yet.
-
She will buy a new laptop.
-
We think they will be late.
-
I will take a break.
Exercises 3:
-
Will you travel next month?
-
Will she study abroad next year?
-
Will they need more time?
-
Will he cook dinner tonight?
-
Will we move to a new office?
Mastering the simple future tense allows you to express plans, predictions, promises, and spontaneous decisions with ease. By understanding its definition, structure, and real-life examples, you can use the simple future tense accurately in both spoken and written English.



.png)







