The past perfect tense is an essential part of English grammar for talking about actions that happened before another moment in the past. It helps you explain past events clearly and avoid confusion.
In this easy guide, you will learn the definition, rules, and examples of the past perfect tense step by step. With support from Monkey, mastering this tense becomes simple and effective for everyday communication.
What is the past perfect tense?
The past perfect tense is used to describe an action that was completed before another action in the past. It helps show the correct order of past events.
We use the past perfect to make it clear that one past action happened earlier than another past action. This avoids confusion when telling stories or explaining situations.
Examples:
-
I had finished my work before she arrived.
-
They had left when we got to the station.
Common time expressions with the past perfect include before, after, by the time, already, and just. These words highlight that the action happened earlier in the past.
Examples:
-
He had already eaten by the time we called him.
-
She had just gone out when it started to rain.
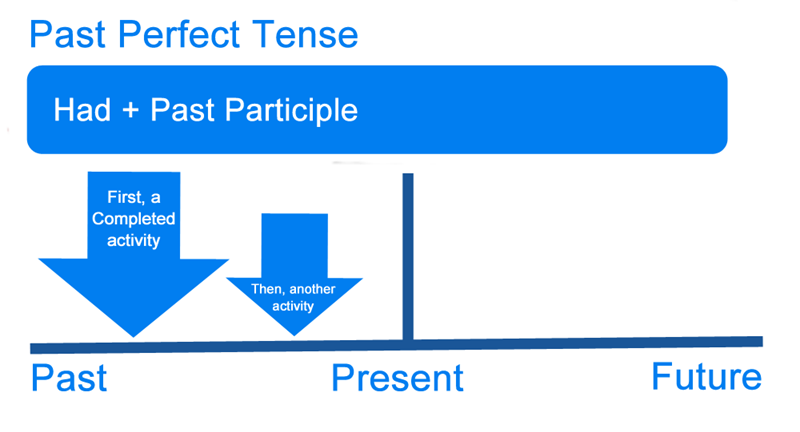
How to form the past perfect tense
The past perfect tense is formed with had and the past participle of the main verb. The structure is the same for all subjects.
1. Affirmative form
Use subject + had + past participle (V3) to state that an action was completed before another past action. This form shows the earlier event clearly.
Examples:
-
I had finished.
-
They had left.
2. Negative form
Use subject + had not (hadn’t) + V3 to say an action had not happened before another past moment. The contraction hadn’t is common in speaking and writing.
Examples:
-
She hadn’t seen it.
-
We hadn’t decided.
3. Question form
Use Had + subject + V3? to ask if an action was completed before another past action. Place had at the beginning of the sentence.
Examples:
-
Had you eaten?
-
Had he arrived?

Uses of the past perfect tense
The past perfect tense is used to show that one action happened earlier than another in the past. It helps make the order of events clear.
1. An action completed before another past action
Use the past perfect to describe an action that finished before a second past action. The second action is usually in the simple past.
Example: She had left before I arrived.
2. An action completed before a specific time in the past
Use the past perfect to say an action was finished before a certain past time. The exact time is often mentioned.
Example: By 8 p.m., they had finished dinner.
3. Cause and result in the past
Use the past perfect to show the cause of a past situation or result. It explains why something happened.
Example: He was tired because he had worked all day.
4. Reported speech and storytelling
Use the past perfect in reported speech and stories to refer to an earlier past event. It helps keep the timeline clear.
Example: She said she had seen the movie before.

Past perfect vs Simple past
The past perfect and the simple past both talk about the past, but they show different time relationships. One highlights the earlier action, while the other shows a completed event.
Comparison table:
|
Criteria |
Past Perfect |
Simple Past |
|
Definition |
Shows an action that happened before another action in the past. |
Shows an action that happened at a finished time in the past. |
|
Focus |
Emphasizes the earlier action in a sequence. |
Emphasizes a completed event or action. |
|
Main Use |
Used to make the time order clear between two past actions. |
Used when the time order is obvious or only one past action is mentioned. |
|
Common Time Markers |
before, after, already, by the time, when + past simple |
yesterday, last night, ago, in 2010, then |
|
Example 1 |
She had finished her work before she went out. |
She finished her work and went out. |
|
Example 2 |
They had left when we arrived. |
They left early last night. |
Past perfect vs Present perfect
The past perfect and the present perfect both use have + past participle, but they point to different times. One looks back from a past moment, while the other connects the past to now.
Comparison table:
|
Criteria |
Past Perfect |
Present Perfect |
|
Definition |
Refers to an action completed before another moment in the past. |
Refers to an action that happened at an unspecified time before now. |
|
Time Focus |
Looks back from a point in the past. |
Connects the past to the present. |
|
Main Use |
Used to show an earlier past event in a sequence. |
Used to show experience, result, or continuity up to now. |
|
Time Markers |
before, after, by the time, already, when (past simple) |
ever, never, already, yet, so far, since, for |
|
Example 1 |
I had finished the report before the meeting started. |
I have finished the report, so we can discuss it now. |
|
Example 2 |
She had lived in Paris before she moved to London. |
She has lived in Paris for three years. |
Practice exercises
Use these exercises to practice the past perfect tense in context. Write your answers before checking them.
1. Fill in the blanks
Complete each sentence using the correct past perfect form of the verb in brackets.
-
She ___ (finish) her homework before dinner.
-
They ___ (leave) by the time we arrived.
-
He ___ (never/see) the ocean before that trip.
-
We ___ (already/eat) when she called.
-
I ___ (lose) my keys before I found them.
2. Choose the correct tense
Choose the correct form: past perfect or simple past.
-
She ___ (had finished / finished) the report before the meeting started.
-
They ___ (had left / left) when we got to the station.
-
He ___ (had studied / studied) hard, so he passed the test.
-
We ___ (had booked / booked) the tickets before the prices went up.
-
I ___ (had seen / saw) that movie last year.
3. Rewrite sentences
Rewrite each sentence using the past perfect.
-
I finished my work. Then I went home.
-
She ate dinner. Then she watched TV.
-
They completed the project. Then the boss arrived.
-
He locked the door. Then he left the house.
-
We packed our bags. Then we went to the airport.
4. Make questions
Change each sentence into a past perfect question.
-
You had finished the task.
-
She had seen the movie before.
-
They had arrived early.
-
He had eaten breakfast.
-
We had decided on a plan.
|
Give your child a strong English foundation from the very beginning with Monkey Junior. Start learning through fun games, native audio, and smart AI tools–perfect for kids aged 0-11. Help them build real skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing step by step. Download Monkey Junior today and watch your child grow in confidence and English ability. |
Answers
Exercises 1:
-
She had finished her homework before dinner.
-
They had left by the time we arrived.
-
He had never seen the ocean before that trip.
-
We had already eaten when she called.
-
I had lost my keys before I found them.
Exercises 2:
-
She had finished the report before the meeting started.
-
They had left when we got to the station.
-
He studied hard, so he passed the test.
-
We had booked the tickets before the prices went up.
-
I saw that movie last year.
Exercises 3:
-
I had finished my work before I went home.
-
She had eaten dinner before she watched TV.
-
They had completed the project before the boss arrived.
-
He had locked the door before he left the house.
-
We had packed our bags before we went to the airport.
Exercises 4:
-
Had you finished the task?
-
Had she seen the movie before?
-
Had they arrived early?
-
Had he eaten breakfast?
-
Had we decided on a plan?

The past perfect tense allows you to show the correct order of past actions with confidence. By understanding its structure and practicing real examples, your English will sound clearer and more natural.
Keep practicing to build strong grammar habits. With helpful lessons from Monkey, you can master the past perfect tense and move closer to fluent English.




.png)